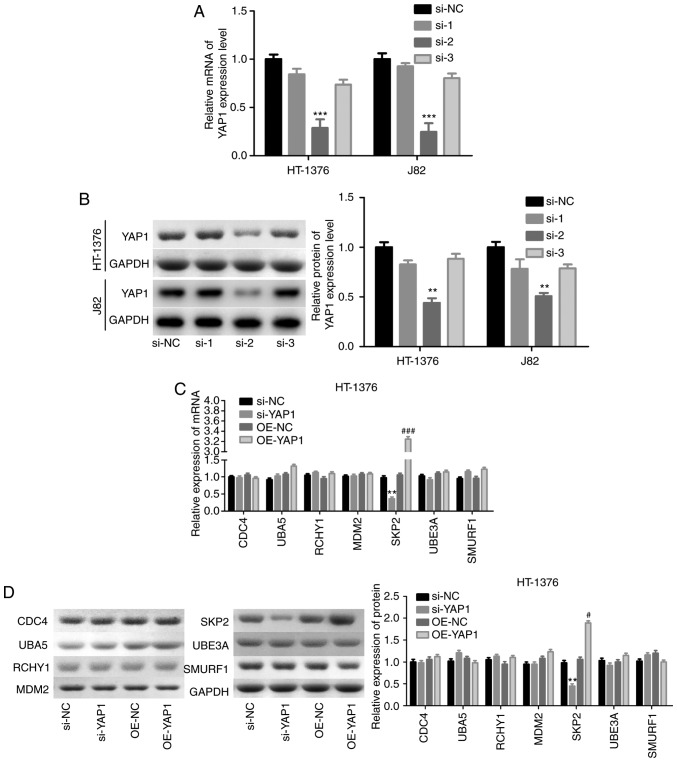
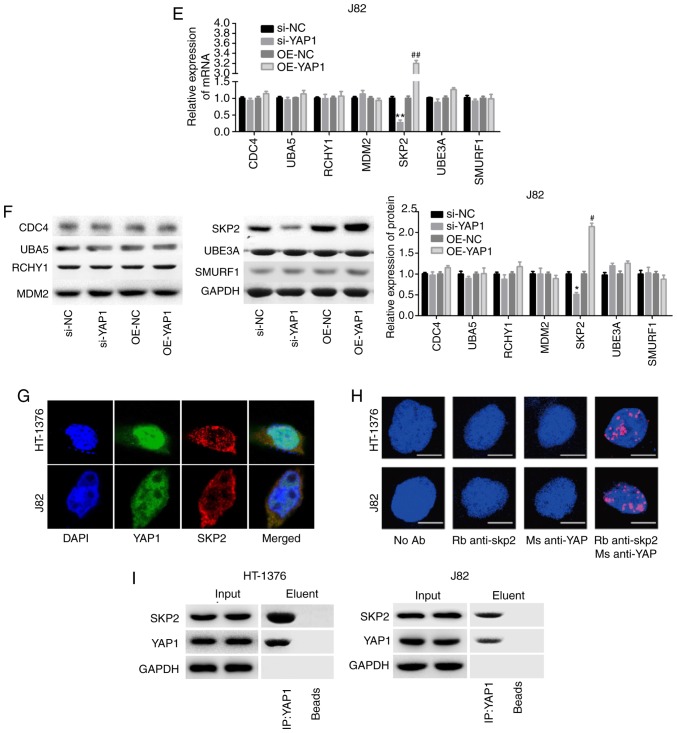
Figure 5.
Detection of the interaction between YAP1 and SKP2. (A and B) HT-1376 and J82 cells were transfected with siRNAs-YAP1; then, cells were harvested and subjected to RT-PCR and western blot assays to determine the knockdown efficiency (**P<0.01, ***P<0.001). After (C and D) HT-1376 and (E and F) J82 cells were transfected with si-YAP1, si-NC, OE-YAP1 and OE-NC, RT-PCR and western blot assays were performed to determine the mRNA and protein levels of CDC4, SKP2, RCHY1, MDM2, UBE3A and SMURF1 (si-YAP1 vs. si-NC group, *P<0.05, **P<0.01; OE-YAP1 vs. OE-NC group, #P<0.05, ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001). (G and H) Immunofluorescence and Duolink assays were performed to evaluate the subcellular localization of the YAP1 and SKP2 proteins. (I) Immunoprecipitation assay was used to assess the combination between YAP1 and SKP2 proteins in HT-1376 and J82 cells ['input' refers to total protein lysate and 'eluent' refers to the immune complex pulled down by YAP1 antibody; beads were used as a negative control (NC)]. YAP1, Yes-associated protein 1; SKP2, S-phase kinase-associated protein 2; RT-PCR, reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction.