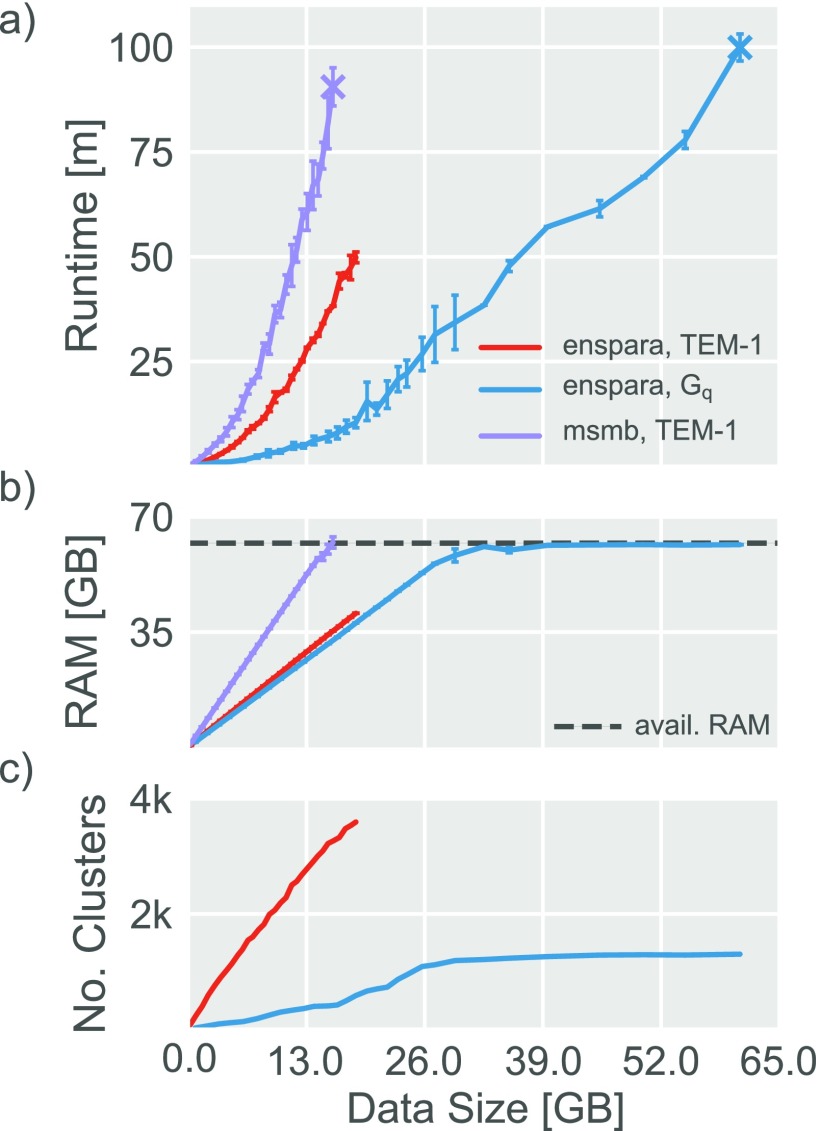
FIG. 4.
The CLI provided by enspara has favorable memory and performance characteristics. (a) Runtime as a function of data input size for the enspara cluster CLI on the TEM-1 and Gq datasets, and the MSMBuilder CLI on the TEM-1 dataset. For TEM-1/MSMBuilder and Gq/enspara, the final point represents the largest data size that can be run without exceeding available memory. (b) Process-allocated memory usage as a function of data input size for the enspara cluster CLI on the TEM-1 and Gq datasets, and the MSMBuilder CLI on the TEM-1 dataset. Apparent memory use by enspara appears to stop growing after 32 GB because, on the computer system tested (see Sec. IV), the operating system allocates double the necessary RAM to enspara. Where MSMBuilder runs out of RAM loading ∼16 GB, enspara is capable of using almost all of the available 64 GB RAM. (c) Number of clusters as a function of data input size for TEM-1 and Gq datasets. The change in runtime growth of the Gq dataset around 26 GB of data loaded is a consequence of the slowdown in state discovery as new data are added. For (a) and (b), error bars represent the standard deviation of three trials.