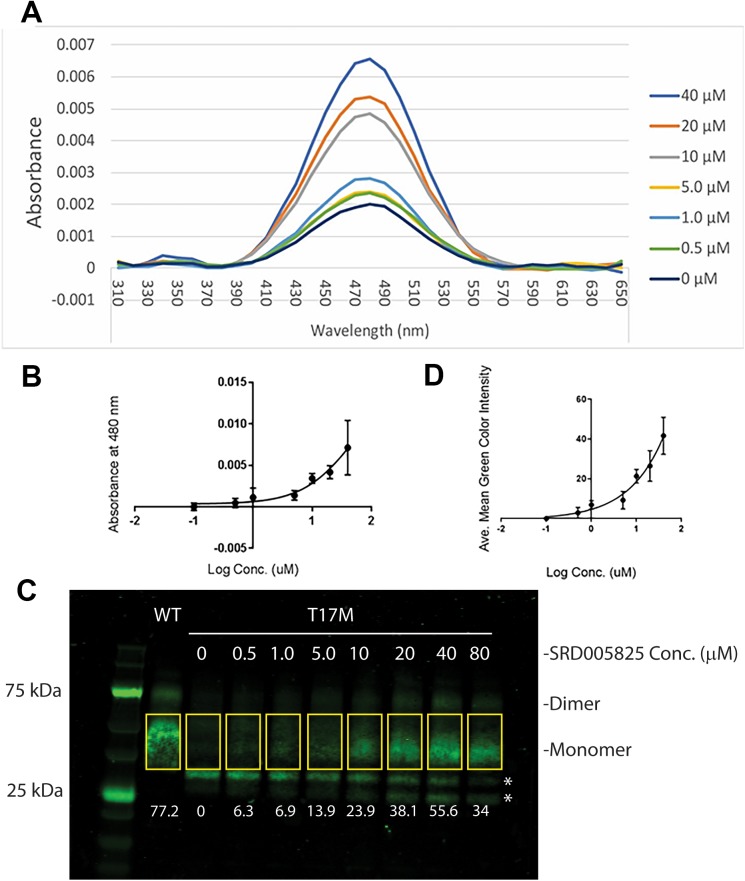
Figure 4.
Generation of functional T17M rhodopsin after treatment with SRD005825. T-Rex-293 cells expressing human T17M opsin were induced for expression and incubated at increasing concentrations of SRD005825. (A) Absorbance spectrum of immunoaffinity-purified T17M rhodopsin from SRD005825-treated T17M-expressing cells, and the rhodopsin peak at 480 nm at increasing concentrations of SRD005825. (B) The plot of OD 480 nm from A as a function of concentration of SRD005825. (C) Western blot using 1D4 antibody of the same T17M rhodopsin samples as in 4 and the comparison to wild-type rhodopsin produced in T-Rex-293 cells. The relative quantities of monomeric T17M opsin were estimated by mean intensity of each band, from three replicates of the experiment (Supplementary Table S1). Numbers at the bottom of each lane represent the mean green color intensity of monomeric T17M opsin within rectangles (using Photoshop CC). Asterisks indicate presumptive proteolytic fragments or nonglycosylated forms of opsin that react with the C-terminal-specific antibody. (D) The plot of relative quantity of T17M rhodopsin as a function of concentration of SRD005825. Due to the toxic effects of SRD005825 at or above 80 μM to the cells, no EC50 could be determined.