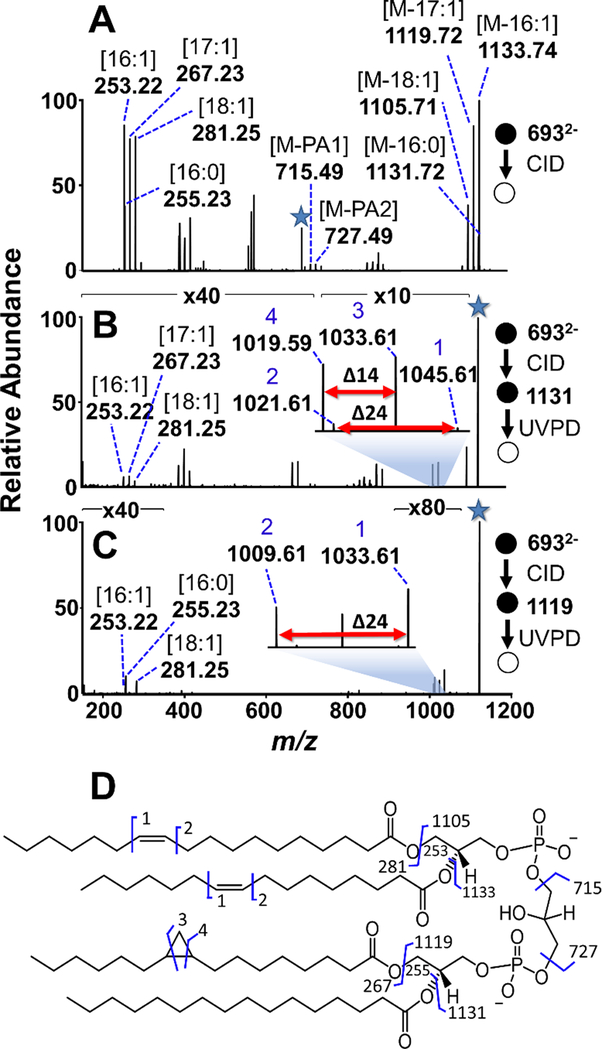
Figure 3:
(A) CID mass spectrum of the ion of m/z 693.48 from E. coli CL extract. (B) UVPD of the m/z 1131.72 fragment ion resulting from the loss of the 16:0 acyl chain yields pairs of diagnostic ions revealing cyclopropyl and double bond positions. (C) UVPD of the m/z 1119.72 fragment ion, corresponding to the loss of a 17:1 acyl chain, results in one pair of diagnostic ions that localize the double bonds to the 16:1 and 18:1 acyl chains. The selected precursor ion in each stage is designated with a star. (D) Fragmentation map constructed from de novo analysis of the CID and CID/UVPD spectra is consistent with CL (18:1(9Δ)_16:1(9Δ))_(17:1(c9Δ)_(16:0)).