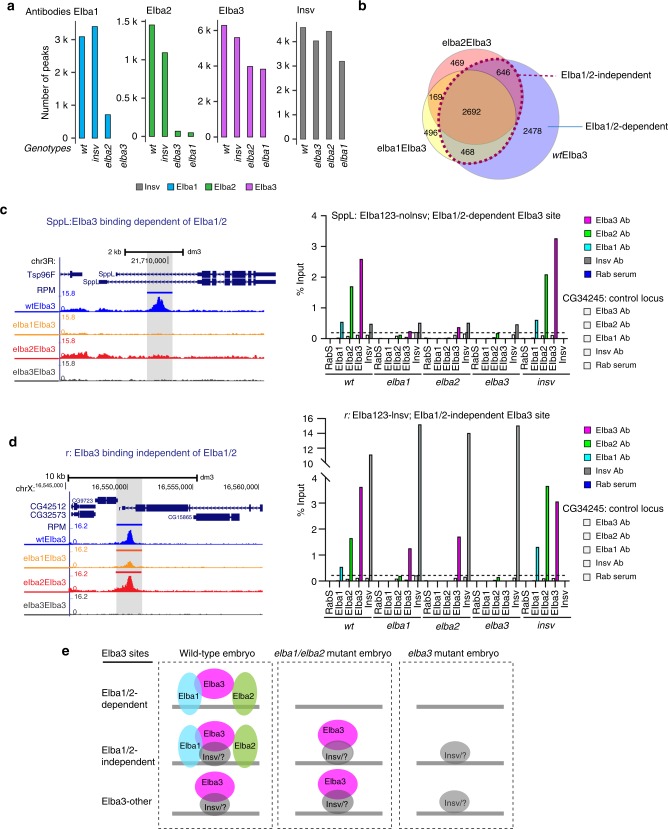
Fig. 2. Elba3-binding sites are partially independent of the ELBA trimeric complex.
a The ChIP-seq peaks of wt and the non-cognate mutants for each factor were called by using the corresponding ChIP-seq reads against the reads in its cognate mutant. The number of peaks is shown for each factor in each genotype. b Overlaps of Elba3 binding in the three genotypes, wt, elba1, and elba2, showing that ~50% wtElba3 sites remain in elba1 and elba2 and are denoted as Elba1/2-independent sites. The wtElba3 sites lost in elba1/2 are Elba1/2-dependent. c ChIP-seq tracks of an exemplary locus SppL, of Elba1/2-dependent sites, are shown on the left. On the right, ChIP-qPCR with a second set of ELBA and Insv antibodies confirms specific enrichment of ELBA in wt and insv mutant embryo, but not in any of the elba mutants. Average value from three technical replicates is plotted. A negative control locus CG34245 was examined in parallel. d An exemplary locus, r, of Elba1/2-independent Elba3 sites. ChIP-qPCR validation using a second set of antibodies against these four factors confirms the ChIP-seq result. e Illustration of three contexts where Elba3 locates to the genome: Elba1/2-dependent, Elba1/2-independent, and other Elba3-binding sites. Source data of the raw qPCR value is available in a Source Data file.