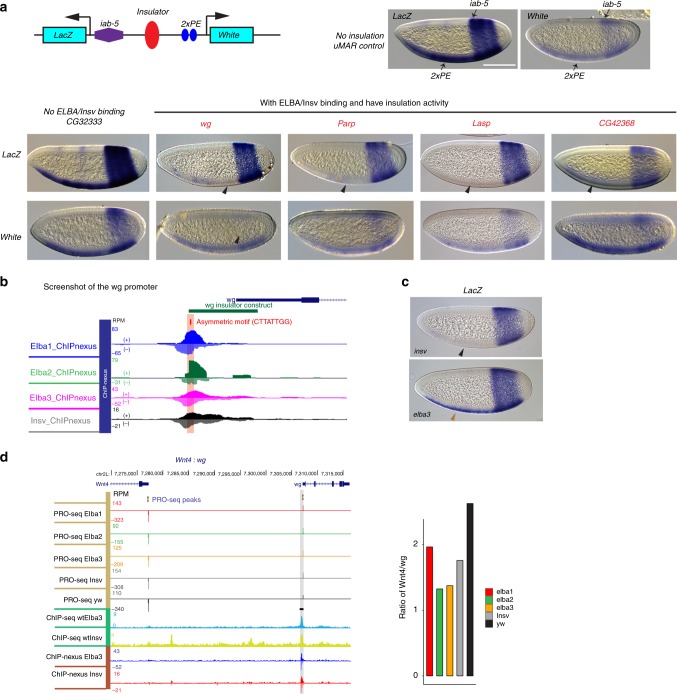
Fig. 7. ELBA is required for separating transcription of Wnt4 and wg.
a Transgenic insulator assay. In situ hybridization images show expression of the lacZ and white genes driven by the 2xPE and iab-5 enhancers in the ventral and the posterior stripes, respectively. An inserted control fragment (uMAR) does not affect the reporter expression, neither does the CG32333 fragment that has no Elba or Insv binding. The fragments from the wg, Parp, and Lasp loci, highlighted in red, show blocking activity, evidenced by loss of the ventral stripe expression of LacZ. The iab-5 enhancer was less affected, with a weaker but visible posterior stripe of white. Black arrowheads indicate the weakened or lost staining by insulation activity of the inserted fragments. b A screenshot of the insulator in the wg locus with ELBA and Insv binding and an asymmetric Insv/ELBA motif. c The lacZ staining shows loss of insulation activity of the wg element in elba3, but not insv mutant embryo. The black arrowhead indicates the absence of the ventral stripe. The brown arrowhead indicates recovery of the ventral stripe due to loss of insulation in the elba3 mutant. d A screenshot of the divergent pair Wnt4 and wg with an Elba/Insv peak proximal to the wg promoter. The ratio of PRO-seq promoter expression of Wnt4 versus wg decreased in the mutants compared with wt. Scale bar: 100 µm.