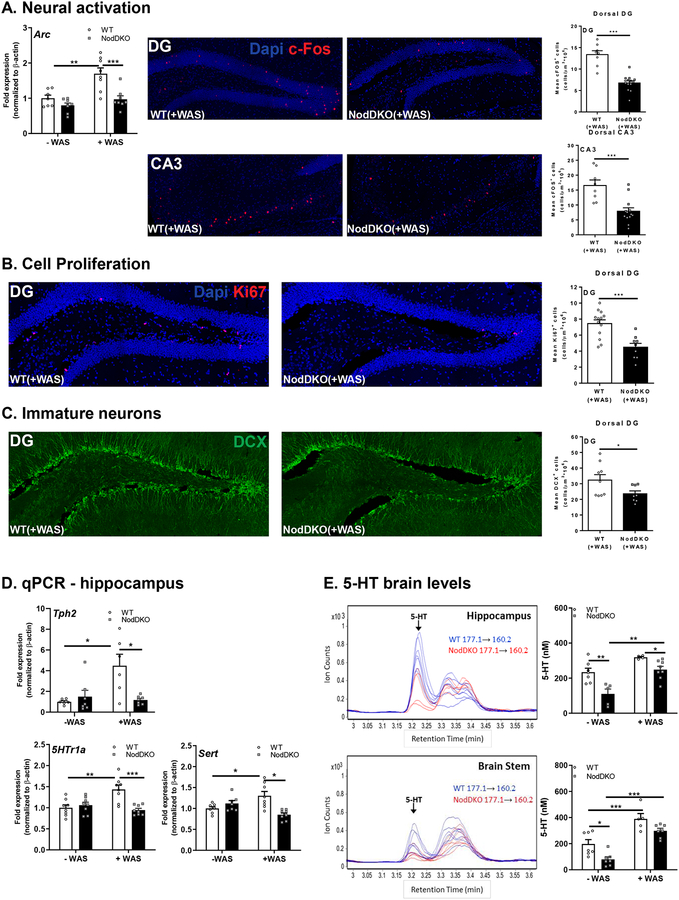
Figure 3. NodDKO(+WAS) mice display decreased neural activation, cell proliferation, and immature neurons, with 5-HT signaling impairments.
(A) Hippocampal Arc mRNA expression levels (N = 7–8), and c-Fos+ cells in the dentate gyrus (DG) (N = 8–13) and the cornus ammonis (CA) 3 regions (N = 8–13) and representative images of c-Fos immunofluorescence; (B) Ki67+ cells (N = 8–13) and representative images of Ki67 immunofluorescence in the DG. (C) DCX+ cells (N = 6–7) and representative images of DCX immunofluorescence in the DG; (D) Tph2, 5HTr1a and Sert hippocampal mRNA expression levels (N = 6–16); (E) serotonin (5-HT) protein levels in the hippocampus (N = 5–8) and brain stem (N = 5–7) detected by LC/MS and multiple reaction monitoring chromatogram of 5-HT in cytoplasmic extracts of both the hippocampus and brain stem: m/z 177.1 correspond to 5-HT precursor ion mass and m/z 160.2 correspond to fragment ion mass. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001, 2-way ANOVA and unpaired Student’s t-test).