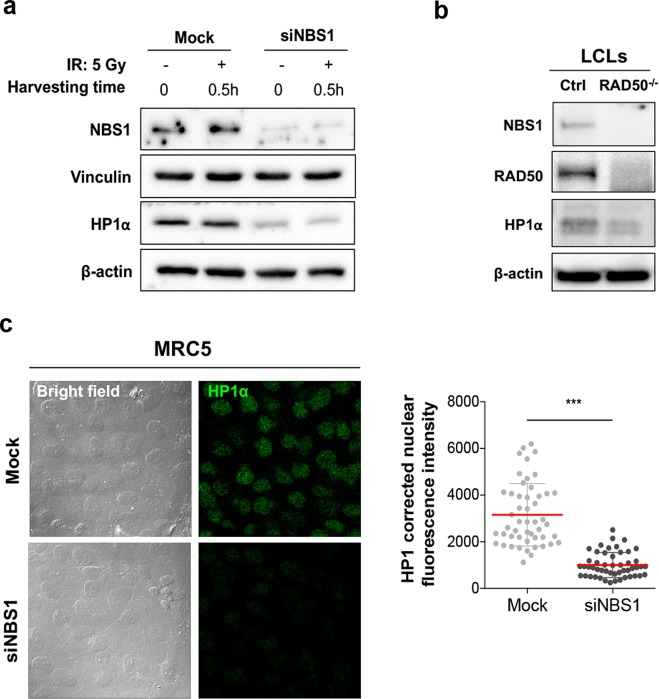
Fig. 5. NBS1 regulates the stability of HP1α.
a WB from both untreated and irradiated mocked and siNBS1– MRC5 cell extracts. Cells were irradiated with 5 Gy of X-rays and harvested after 0.5 h. Ten micrograms of total protein lysates were analyzed by WB. Membranes were probed with anti-HP1α and anti-NBS1 antibodies; vinculin and β-actin were used as loading controls. b WB from extracts of lymphoblastoid cells (LCLs) established from an healthy donor (Ctrl) and from a patient carrying two germline mutations in the RAD50 gene (RAD50−/−)30. Membranes were probed with anti-HP1α, anti-NBS1, and anti-RAD50 antibodies; β-actin was used as loading control. c Left: representative images of the immunofluorescence analysis of HP1α (Alexa Fluor 480, green fluorophore green) protein levels in mocked and NBS1-silecenced MRC5 cells. Bar: 20 μm. Right: Distribution of HP1α corrected nuclear fluorescence intensity in mocked and NBS1-silecenced MRC5 cells. The horizontal lanes indicate the mean values derived from the analysis of 100 cells/experimental point in three independent experiments ±S.D. (t Student’s Test; ***p < 0.001).