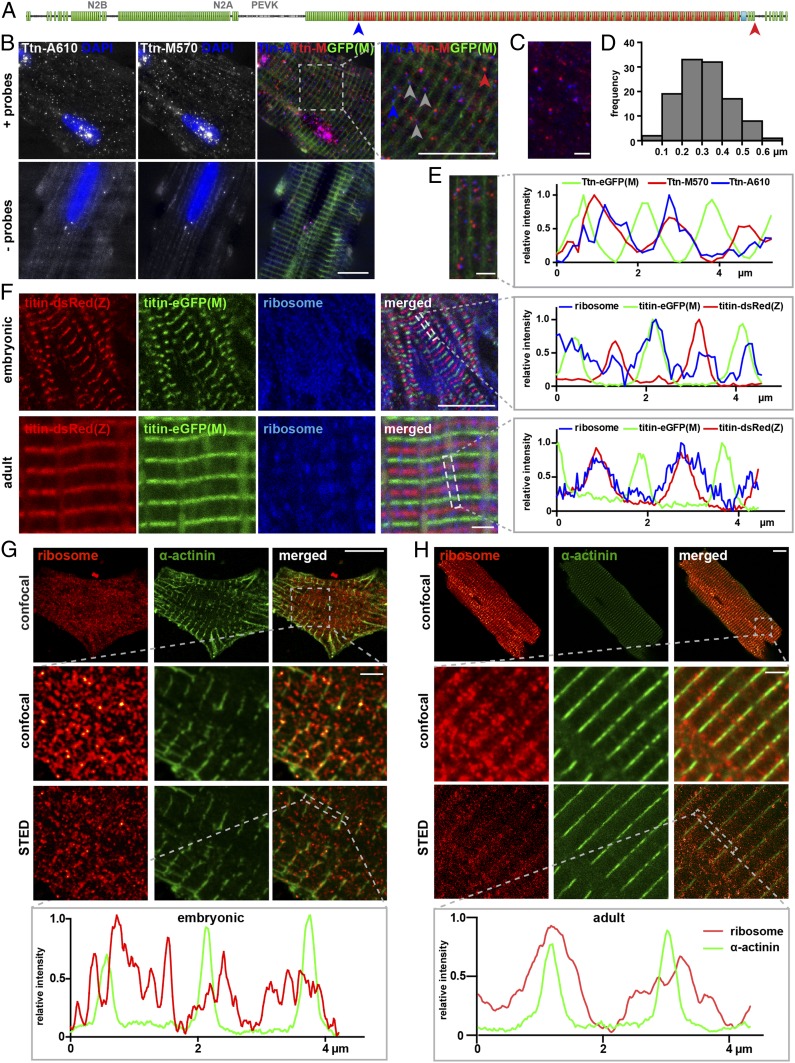
Fig. 2.
Sites of sarcomeric protein synthesis differ between embryonic and mature cardiomyocytes with titin mRNA and ribosomes localized toward the Z-disk in adults. (A) FISH probes were directed against the titin A-band and M-band region, respectively. (B) Localization of titin mRNA in titin-eGFP(M) adult cardiomyocytes. The probes detect single titin molecules. (Scale bar: 10 µm.) Ttn-A (blue) and Ttn-M (red) probes localize in close proximity, but not directly on top of each other as expected for background (Bottom). (C and D) The distance between Ttn-A and Ttn-M probe was measured in 4 regions of 4 different cells. (Scale bar: 2 µm.) (E) Straightened and stitched sarcomere segments of a representative cell. (Scale bar: 2 µm.) Localization of titin FISH probes relative to the M-band in line profile diagrams. (F) In embryonic cardiomyocytes, ribosomes distribute evenly along the myofiber. (Scale bar: 10 µm.) In adult cardiomyocytes, ribosomes are clustered around the Z-disk. Confocal images. (Scale bar: 2 µm.) (G) Superresolution microscopy (STED) of embryonic wild-type cardiomyocytes confirms localization of the ribosomes throughout the cytoplasm (α-actinin; green). (Scale bar: Top, overview, 10 µm; Middle and Bottom, 2 µm.) (H) In adult cardiomyocytes, ribosomes are localized at the Z-disk and extend into the I-band. At the Z-disk, α- actinin and ribosome signals overlay. (Scale bar: Top, overview, 10 µm; Middle and Bottom, 2 µm.) The localization of ribosomes is indicated as a line profile along the dotted rectangle.