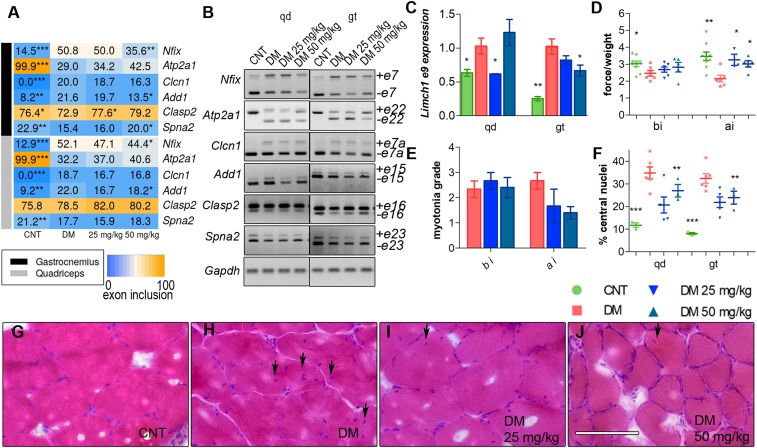
Fig. 7.
Injection (i.p.) of CQ improves Mbnl-regulated splicing and muscle function and histopathology of HSALR mice. (A) Heatmap representing the analysis of splicing decisions altered in HSALR mice. The number in the boxes indicates the percentage of inclusion of the indicated exons obtained by semiquantitative RT-PCR. (B) Representative gels used to perform quantifications in A from quadriceps (qd) (Left) and gastrocnemius (gt) (Right) muscles. (C) RT-qPCR to analyze exon 9 inclusion of Limch1. Gadph values were used for normalization in the quantification of the percentage of exon inclusion. (D) Forelimb grip strength and (E) myotonia grade measured before injection (bi) and 7 d after the last dose (ai). All comparisons are relative to HSALR mice treated with the vehicle PBS (DM). (F) Quantification of the percentage of central nuclei in muscle fibers from qd and gt muscles. (G–J) Representative micrographs of muscle fibers stained with H&E and quantified in F. (Scale bar, 100 µm.) Experimental groups were control (CNT) (FVB; n = 8), DM (HSALR; n = 6), DM 25 mg/kg (HSALR; n = 3), and DM 50 mg/kg (HSALR; n = 5). All comparisons are relative to HSALR mice treated with the vehicle PBS (DM). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 according to Student’s t test.