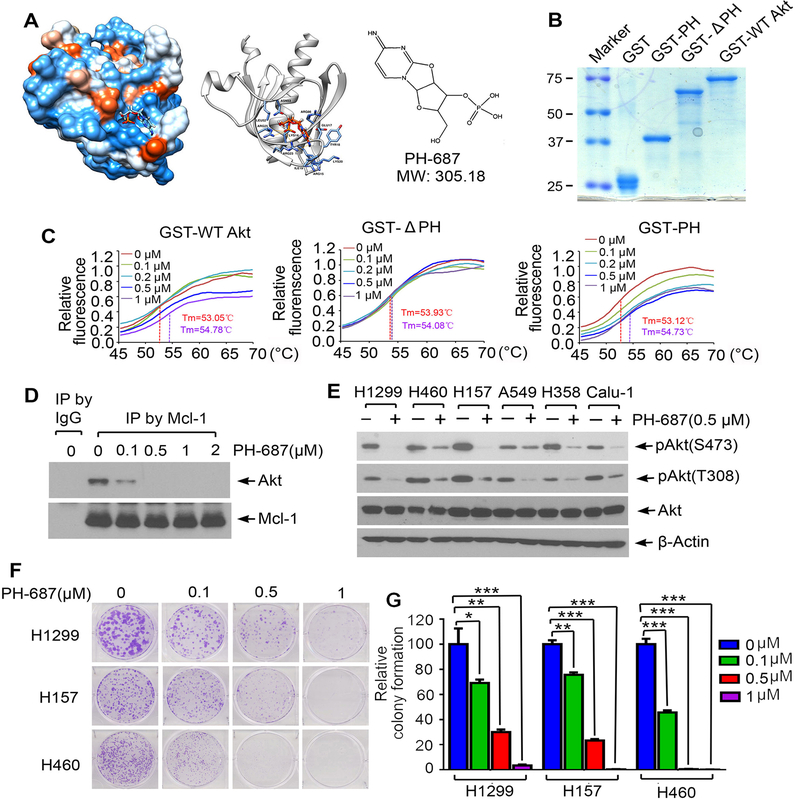
Figure 6.
Discovery of small molecule PH-687 as a lead compound that specifically binds to the PH domain of Akt, disrupts Mcl-1/Akt interaction and reduces Akt activity. A, Structural modeling of small molecule PH-687 in the PH domain binding pocket of Akt protein. B, Recombinant GST-PH, GST-ΔPH and GST-WT Akt recombinant proteins were purified from Escherichia coli Rosetta using glutathione sepharose column. Proteins were stained by Coomassie blue. C, Thermal shift melting curve of purified GST-WT Akt, GST-ΔPH and GST-PH-only proteins incubated with increasing concentrations of PH-687. Melting temperature (Tm) values of 0μM and 1μM of PH-687 are shown. D, H1299 cells were treated with increasing concentrations of PH-687 for 24h, followed by co-IP using Mcl-1 antibody and Western blot with Akt or Mcl-1 antibody, respectively. E, Various lung cancer cell lines were treated with PH-687 (0.5 μM) for 24h, followed by analysis of pAkt by Western blot. F and G, Colony formation assay of H1299, H157 and H460 cells following treatment with increasing concentrations of PH-687. Data represent the mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, by 2-tailed t test.