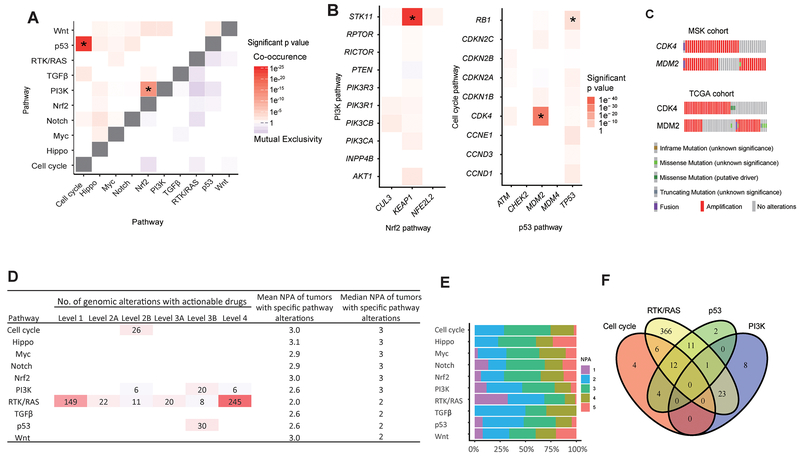
Figure 4. Mutual exclusivity, co-occurrence, and therapeutic actionability.
A, Co-occurrence and mutual exclusivity between pathways. Asterisk indicates the P value is significant (P<0.001, adjusted using the false discovery rate method). Color scale shows the significance of co-occurrence or mutual exclusivity (-log P value). B, Co-occurrence and mutual exclusivity of single genes within PI3K-Nrf2 pathways and p53–cell cycle pathways. Asterisk indicates the P value is significant (CDK4-MDM2, P<0.001; RB1-TP53, P=0.03; STK11-KEAP1, P<0.001). C, Oncoprint of the CDK4-MDM2 altered patients in this study and the TCGA pan-cancer atlas cohort. D, Actionable genetic alterations within 10 pathways annotated using OncoKB and mean/median number of pathway alterations (NPA) for each pathway. E, Stacked bar plot of percentage of NPA (x-axis) in patients with specific pathway (y-axis) altered. F, Venn diagram showing patients who have actionable alterations in the 4 indicated pathways. Intersections of the circles show the number of patients who have >1 actionable pathway.