Figure 6: HRAN improves detection of task-driven voxels.
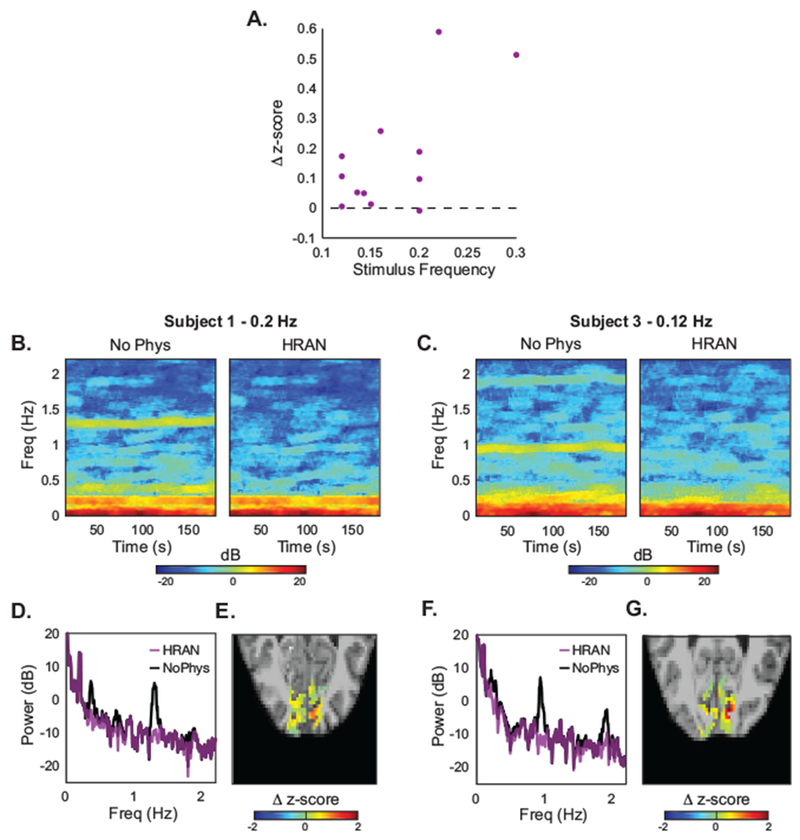
(A) As compared with no physiological regression, HRAN increases the median z-scores of anatomically and functionally defined ROIs in visual cortex across four subjects and twelve runs. Autoregressive noise was not removed. (B, C) Spectrograms of this ROI are shown with and without physiological noise removal in two exemplar runs, demonstrating that respiratory and cardiac frequencies are selectively removed. (D, F) Power spectra in these two exemplar runs further illustrates that these physiological peaks are removed, while the signal and background noise is preserved. (E, G) Maps of the differences in z-scores in each voxel of an example slice with and without HRAN, showing broad increases in statistical detection of activation across the visual cortex when HRAN is applied.
