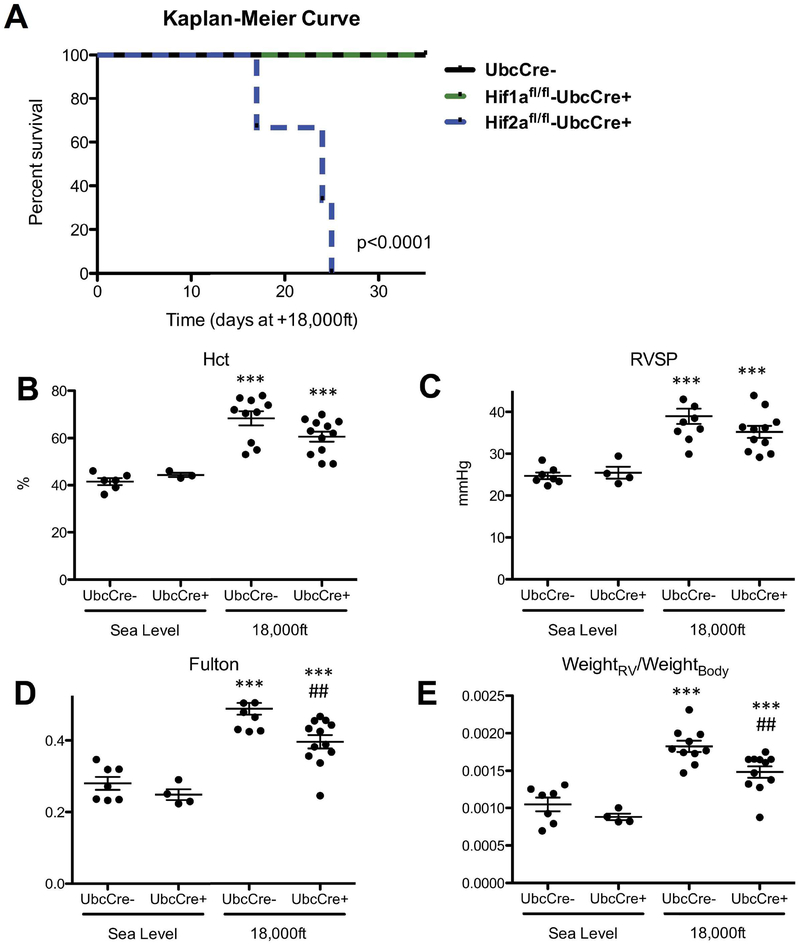
Figure 2: Global Hif2α gene deletion is incompatible for mouse survival under hypoxic conditions while global partial Hif2α gene deletion diminishes hypoxia-induced PH development at 5 weeks in adult mice.
Mice were treated with tamoxifen and exposed to normoxia or hypoxia as described in Fig 1A. A) Kaplan-Meier-Curve for survival of Hif2αfl/fl;UBC-CreERT+ mice during hypoxia exposure, compared to survival of Hif1αfl/fl;UBC-CreERT+ and Hif2αfl/fl;UBC-CreERT− mice during exposure to hypoxia. More than 9 mice in each group were used for this experiment. B–E: Hemodynamics of Hif2αfl/WT;UbcCreERT+ and Hif2αfl/WT;UbcCreER− mice after 5 week exposure to normoxia or hypoxia. B) Hematocrit (Hct) levels. C) RVSP. D) Fulton index. E) ratio of RV-weight to bodyweight. # is used to show the differences between genotypes or treatments under hypoxic condition in this and all other figures of this study. Statistical analysis showed here is 2-way ANOVA analysis (note in panel C there is a significant decrease in RVSP at 18,000 in UbcCre+ animals analyzed by unpaired T-test p<0.05).