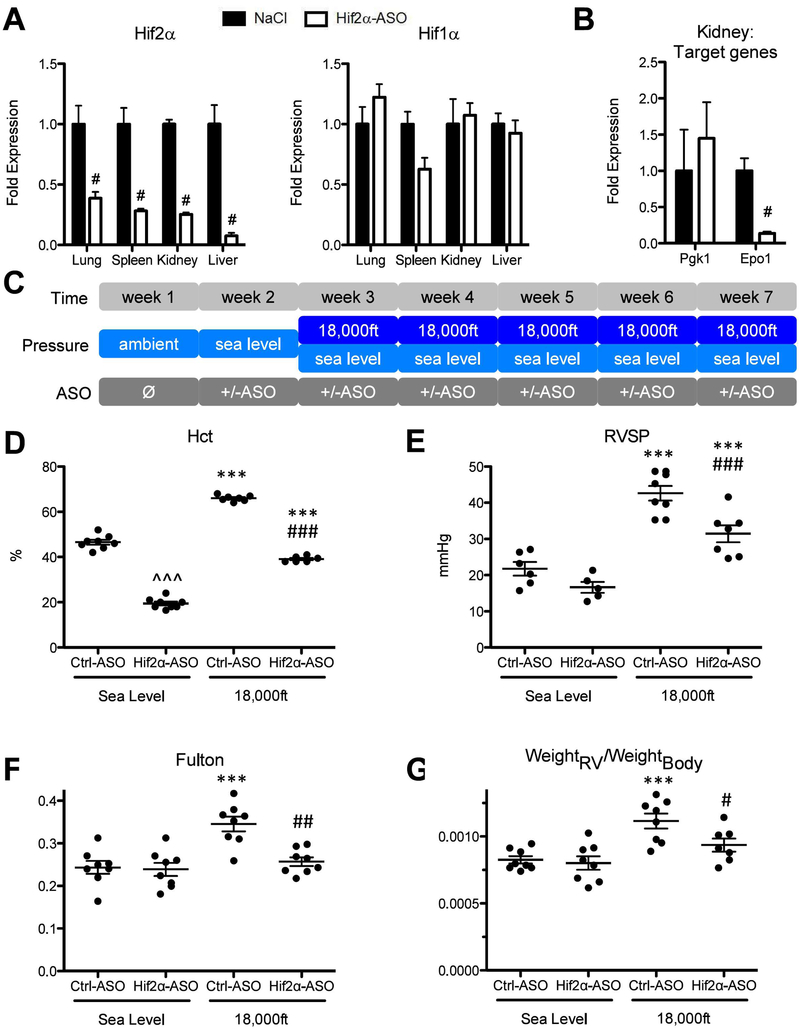
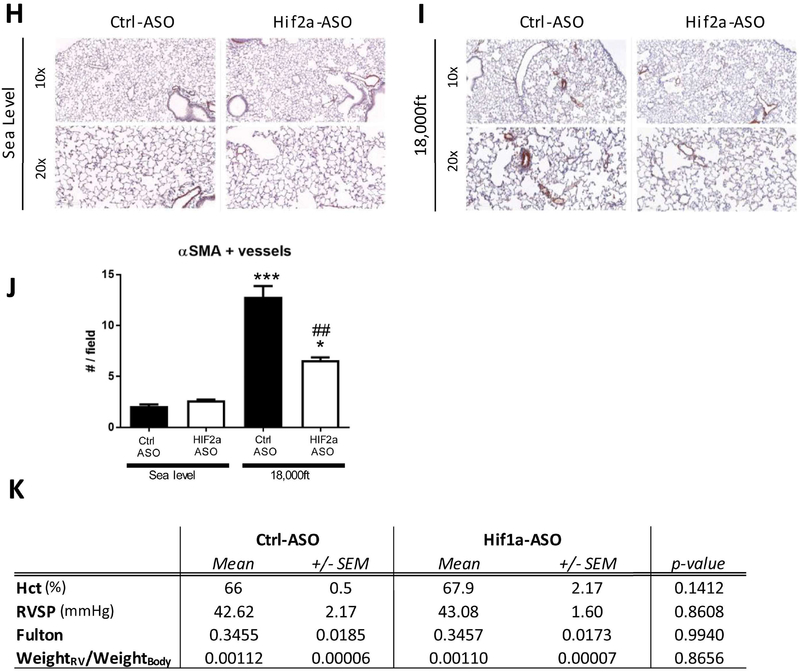
Figure 3: Knockdown of Hif2α but not Hif1α utilizing antisense-oligonucleotides significantly reduces development of hypoxia-induced PH at 5 weeks in adult mice.
A and B) Testing the effectiveness and specificity of antisense-oligonucleotide in a pilot experiment. Wild-type C57bl/6J mice were treated either with injections of an antisense-oligonucleotide targeting Hif2α mRNA (Hif2α-ASO) or equal volumes of 0.9% NaCl (Ctrl) at days 1, 4, 8 and 11. At day 12, mice (N=3) were sacrificed and multiple organs were collected for RNA preparation. A) Levels of Hif1α and of Hif2α mRNA were quantified by qRT-PCR in indicated organs. B) Levels of Pgk1 (a HIF1 target gene) and Epo (a HIF2 target gene) in kidneys from mice targeted with NaCL or Hif2α-ASO, were quantified by qRT-PCR. C) Experimental setup. In week 2, mice were kept under sea level and began to receiving injection of Control, Hif1α-ASO, or Hif2α-ASO (two injections per week at Monday and Thursday). Starting week three, mice were exposed to either sea level or 18,000ft for 5 weeks, in which two injections per week were maintained. D–K) Endpoint measurements for the experimental animals in C. D) Hct. E) RVSP. F) Fulton index. G) ratio of RV-weight to bodyweight. H–J) alpha-SM-actin positive pulmonary vessels. K) Summary of Hct, RVSP, Fulton index, ratio of RV-weight to bodyweight for mice targeted with control or Hif1α-ASO under normoxia or hypoxia. Statistical significance as determined by t-test (A, B, J, and K) or 2-way ANOVA (D–G). ^ is used to show the differences between genotypes or treatments under normoxic condition in this and all other figures of this study.