Figure 2. Fo5176‐induced depletion of the cellulose synthase machinery and acidification of the plasma membrane interface can be buffered and are dependent on upregulation of AHA activity.
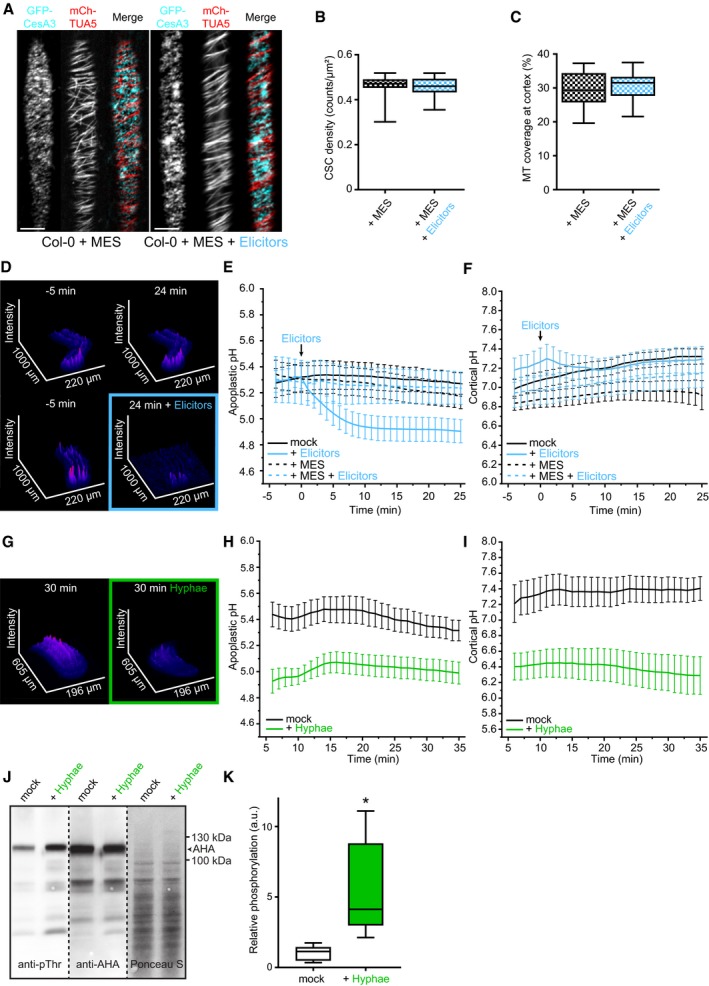
- Representative image of a 5‐day‐old WT (Col‐0) GFP‐CesA3 and mCh‐TUA5 dual‐labeled root epidermal cell in half MS + 5 mM MES (left panel) or upon 5‐min elicitor treatment in half MS + 5 mM MES (right panel). Scale bar = 5 μm.
- GFP‐CesA3 density at the plasma membrane after elicitor treatment in half MS + 5 mM MES as depicted in (A). Box plots: centerlines show the medians; box limits indicate the 25th and 75th percentiles; whiskers extend to the minimum and maximum. N ≥ 35 cells from 10 roots and three independent experiments.
- Microtubule density at the cell cortex after elicitor treatment in half MS + 5 mM MES as depicted in (A). Box plots as described in (B). N ≥ 29 cells from 10 roots and three independent experiments.
- Representative surface plot of a WT root expressing the pHapo sensor SYP122‐pHusion grown in half MS (−5 to 0 min). At 0 min, either H2O (upper panel) or an elicitor mix (lower panel) was added. Upon elicitor treatment, the signal intensity in the depicted 488 nm channel drastically decreases (highlighted with a blue square).
- Apoplastic pH in WT roots expressing the pHapo sensor SYP122‐pHusion over time, either in half MS or in half MS + 5 mM MES. Imaging started 5 min before either H2O or a fungal elicitor mix was added (0 min). Values are mean ± SEM, N ≥ 15 seedlings from three independent experiments. RM two‐way ANOVA on half MS + H2O versus half MS + elicitors: P ≤ 0.05 (treatment), P ≤ 0.001 (time), P ≤ 0.001 (treatment × time).
- Cortical pH of WT roots expressing the pHcortical sensor pHGFP‐Lti6b over time, either in half MS or in half MS + 5 mM MES. Imaging started 5 min before either H2O or a fungal elicitor mix was added (0 min). Values are mean ± SEM, N = 16 seedlings from three independent experiments. Mixed‐effects model on half MS + H2O versus half MS + elicitors: P = 0.80 (treatment), P ≤ 0.001 (time), P ≤ 0.001 (treatment × time).
- Representative surface plot of WT root expressing the pHapo sensor SYP122‐pHusion grown 30 min in half MS (left panel) or half MS + Fo5176 hyphae (right panel). The hyphae treated root shows drastically reduced signal intensity in the depicted 488 nm channel (highlighted with a green square).
- Apoplastic pH of WT roots expressing the pHapo sensor SYP122‐pHusion over time, either in half MS or half MS + Fo5176 hyphae. Roots were exposed to hyphae for 5 min before imaging started. Values are mean ± SEM, N ≥ 12 seedlings from three independent experiments. RM two‐way ANOVA on half MS versus half MS + elicitors: P ≤ 0.01 (treatment), P ≤ 0.001 (time), P ≤ 0.001 (treatment × time).
- Cortical pH variation of WT roots expressing the pHcortical sensor pHGFP‐Lti6b over time, either in half MS or in half MS + Fo5176 hyphae. Roots were exposed to hyphae for 5 min before imaging started. Values are mean ± SEM, N ≥ 13 seedlings from three independent experiments. RM two‐way ANOVA on half MS versus half MS + elicitors: P ≤ 0.01 (treatment), P = 0.23 (time), P ≤ 0.001 (treatment × time).
- Western blots showing chemiluminescent signals of an anti‐pThr or anti‐AHA incubated membrane loaded with Arabidopsis root samples treated for 8 min with either half MS or half MS + Fo5176 hyphae. The Ponceau S panel shows total protein content. The AHA band used for quantification is indicated with an arrowhead. Dashed line separates different treatments of the same membrane.
- Relative AHA phosphorylation status from Western blots as shown in (J). Normalized signal intensity ratio of anti‐pThr in respect to anti‐AHA is shown. Box plots as described in (B). N = 5 independent experiments. Welch's unpaired t‐test; *P‐value ≤ 0.05.
Source data are available online for this figure.
