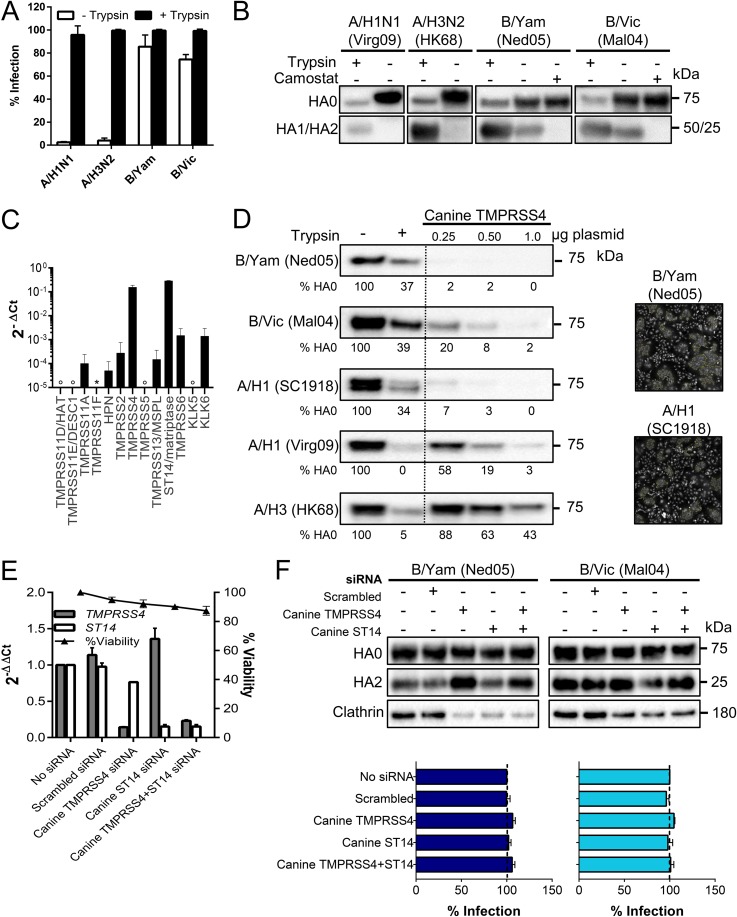
FIG 6.
MDCK cells contain high levels of HA-activating TMPRSS4. (A and B) IAV or IBV replication in MDCK cells in the presence or absence of trypsin. (A) Percentage of infected cells at day 3 p.i., quantified by high-content imaging of NP. Values are means ± SEM of two experiments performed in quadruple. (B) HA0 cleavage state at day 3 p.i. in cells receiving 0 or 10 μM camostat. (C) Expression of TTSP and KLK proteases in MDCK cells (normalized to canine GAPDH and HMBS). Open circle, undetermined; *, no data (no canine mRNA sequence was available to design primers). (D) Canine TMPRSS4 activates the HAs of IAV and IBV. Western blot lanes, from left to right, are as follows: HA0 band in HEK293T cells receiving no protease, exogenous trypsin, or the canine TMPRSS4 plasmid at three different concentrations. Under each lane, the HA0 band intensity is given (normalized to that of clathrin and expressed relative to the no-trypsin condition). Photographs show polykaryon formation in HeLa cells undergoing coexpression of HA and canine TMPRSS4. (E and F) Effect of TMPRSS4 and/or ST14/matriptase knockdown in MDCK cells. (E) mRNA levels at 24 h after siRNA transfection, normalized to the levels of canine HMBS and GAPDH and shown as the fold change relative to the level in the untransfected control. (F) siRNA-transfected cells were infected with B/Yam or B/Vic virus; at day 3 p.i., the HA0 cleavage state was determined by Western blotting, and virus infection was assessed by high-content imaging of NP.