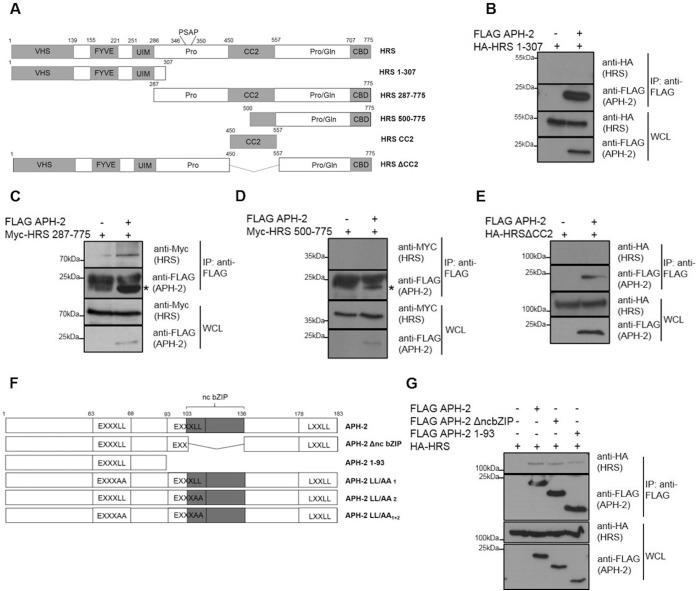
FIG 2.
HRS interacts with the N terminus of APH-2 via its CC2 domain. (A) Schematic representation of the functional domains in HRS and the deletion mutants used in this study. VHS, VPS27-Hrs-STAM; FYVE, FYVE zinc finger domain; UIM, ubiquitin interaction motif; Pro, proline-rich domain containing the PSAP motif; CC2, coiled-coil domain; Pro/Gln, proline- and glutamine-rich domain; CBD, clathrin-binding domain. (B to E) HEK293T cells were cotransfected with FLAG-APH2 or empty plasmid and the indicated HRS deletion plasmids. Cellular lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation using an anti-FLAG M2 resin, and interactions were analyzed by Western blotting using anti-FLAG, anti-HA, and anti-Myc antibodies. The asterisks indicate the band for FLAG-APH-2. (F) Schematic representation of full-length APH-2 and deletion mutants used in this study. Functional domains are indicated, as follows: EXXXLL, endosomal trafficking motif; ncbZIP, nonconventional basic leucine zipper domain; LXXLL, LXXLL motif. (G) Coimmunoprecipitations with lysates from HEK293T cells cotransfected with HA-HRS and the indicated FLAG-APH-2 deletion mutants were performed using anti FLAG-M2 resin. Antibodies against HA and FLAG epitopes were used to analyze interactions. IP, immunoprecipitation; WCL, whole-cell lysate.