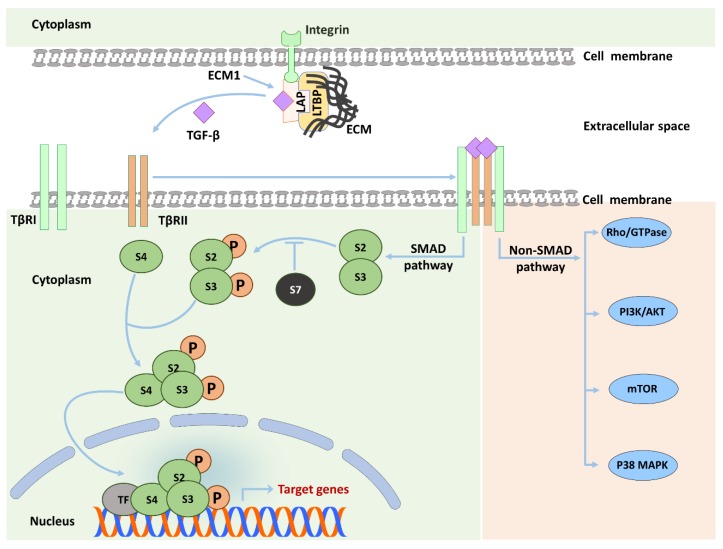
Figure 2.
SMAD- and Non-SMAD-dependent TGF-β signaling. Upon liver damage associated signaling, TGF-β molecules are freed from the large latent complex (LLC) through the interaction of integrins with the latent association protein (LAP). Binding of released TGF-β to TβRII results in the formation of a heterotetramer with TβRI, which then initiates the canonical signaling pathway through phosphorylation of R-SMADs, i.e., SMAD2 (S2) and SMAD3 (S3). TGF-β can also activate non-canonical SMAD-independent pathways, as exemplified here by MAPK, mTOR, PI3K/AKT, and Rho/GTPase pathways. Alongside other mechanisms, SMAD7 negatively regulates TGF-β signaling through competing with R-SMADs for TβRI binding. TF: Transcription factors, P: phosphate group, LTBP: latent TGF-β binding protein.