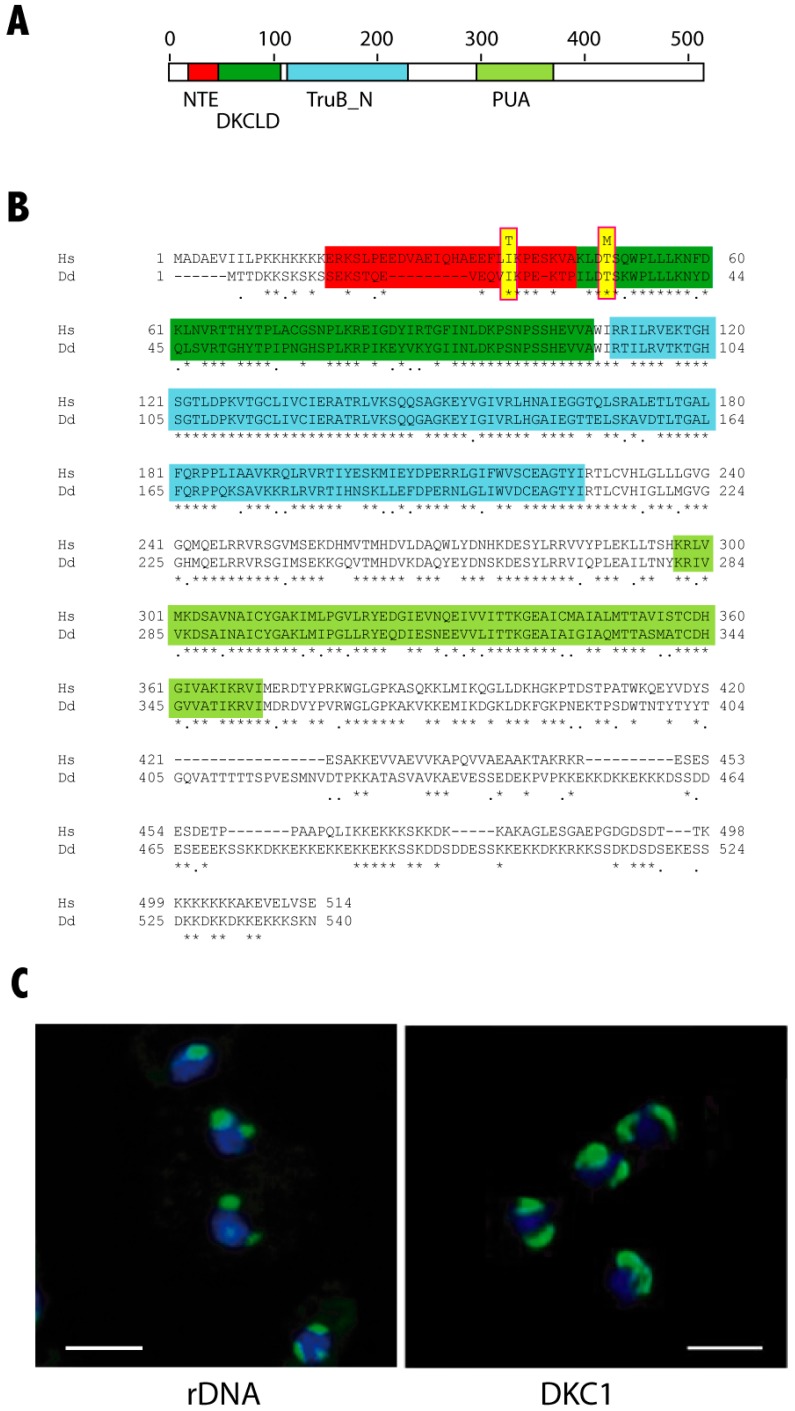
Figure 1.
Protein sequence and expression of D. discoideum dyskerin, (A) Schematic representation of dyskerin conserved domains. The conserved domains N-terminal extension (NTE), dyskerin-like domain (DSKLD), pseudouridin synthase catalytic domain (TruB_N) and RNA-binding domain (PUA) are represented according to the human protein. Amino acid positions are shown in the upper part of the diagram. (B) Comparison of the human (Hs) and D. discoideum (Dd) dyskerin amino acid sequences. Functional conserved domains are indicated using the same color code as in Panel A. The amino acids mutated in the D. discodeum protein in this study are highlighted in yellow. (C) D. discoideum nucleoli, one or two in each cell, were identified in the left panel by hybridization with a probe specific for the 26S ribosomal RNA. The right panel shows the expression of a D. discoideum dyskerin-GFP fusion protein after transfection of the cells with a dyskerin expression vector. Nuclei were stained with DAPI and are shown in blue color. Scale bars correspond to a distance of 5 μm.