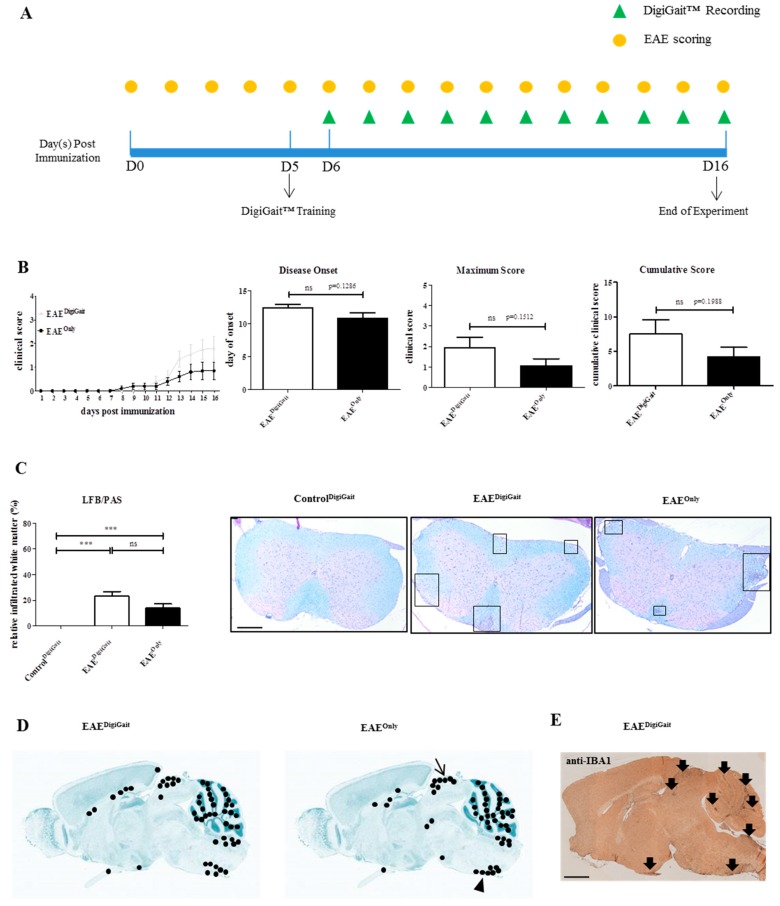
Figure 2.
Manipulation during DigiGait™ recordings does not ameliorate EAE severity. (A) Schematic depiction of the experimental setup. D = days post immunization. The yellow circles indicate time points when EAE scoring was performed. The green triangles indicate time points when DigiGaitTM-measurements were performed. Note that at day 5 post immunization (D5), one DigiGaitTM training session was conducted. (B) Clinical course and evaluation of the disease parameters disease onset, maximum score, and cumulative score in EAEDigiGait (n = 10) and EAEOnly (n = 10) mice. Note that 8 EAEDigiGait and 6 EAEOnly mice, which developed clinical disease, were included to calculate the parameter disease onset. Data from all mice were included to calculate the parameters maximum score and cumulative score. Statistical comparison was done using an unpaired t-test. (C) Extent of inflammatory demyelination among ControlDigiGait, EAEDigiGait, and EAEOnly mice evaluated in LFB/PAS stained sections (n = 72 sections). Black boxes highlight the inflammatory foci. Statistical comparison was done using a one-way analysis of variance with the obtained p-values corrected for multiple testing using the Dunnett’s post hoc test. (D) Cumulative map of the spatial distribution of microgliosis in the CNS of EAEDigiGait and EAEOnly mice, visualized by anti-IBA1 stains. Twenty sections from 10 individual animals were included per group. Each black dot shows the position of a focal IBA1+ lesion which was identified by both evaluators (J.Z. and H.K.). (E) Representative anti-IBA1 stain demonstrating IBA1+ lesions in an EAEDigiGait mouse. Scale bar (C) = 300 µm; Scale bar (E) = 1 mm. EAE: Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis; LFB/PAS: Luxol fast blue/periodic acid-Schiff; CNS: Central Nervous System; IBA1: ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1. *** p ≤ 0.001, ns = not significant.