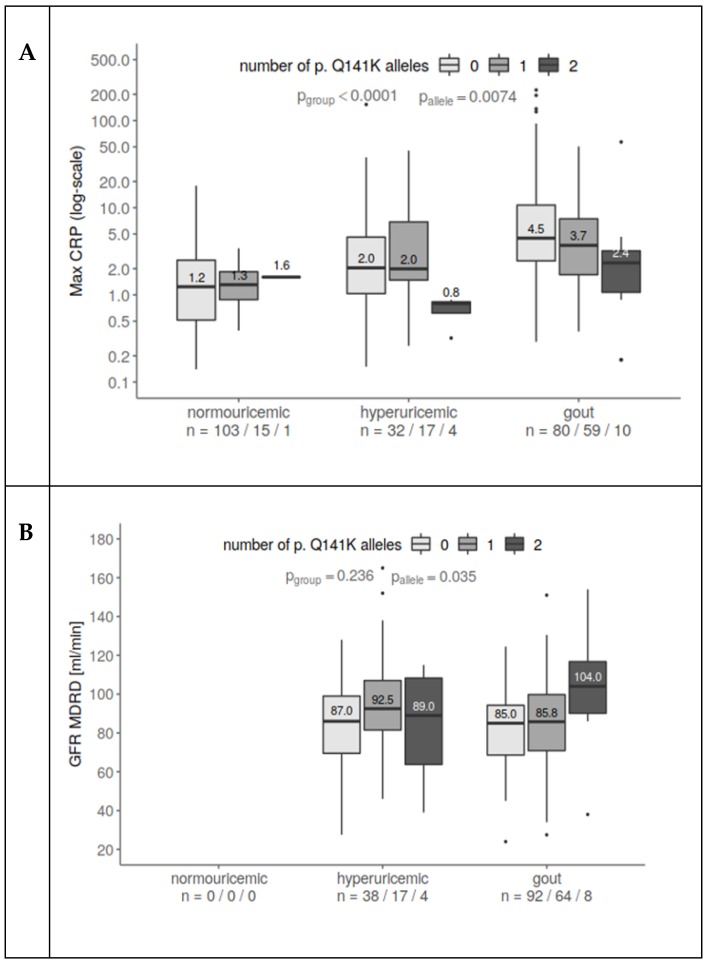
Figure 2.
The connection between the presence of p.Q141K, maximum CRP, and eGFR-MDRD. (A) CRP increased with hyperuricemia and even more for gout patients compared to normouricemic subjects. At the same time, p.Q141K homozygotes had lower CRP than heterozygotes and wild type. The relationship prevailed after including age as a covariate (CRP slightly rises with subject age). (B) GFR increases with an increasing number of p.Q141K alleles, in a similar way for both hyperuricemic and gout patients. One extreme observation (426 mL/min) was excluded since it heavily influenced the fit. All values were log-transformed for a better fit.