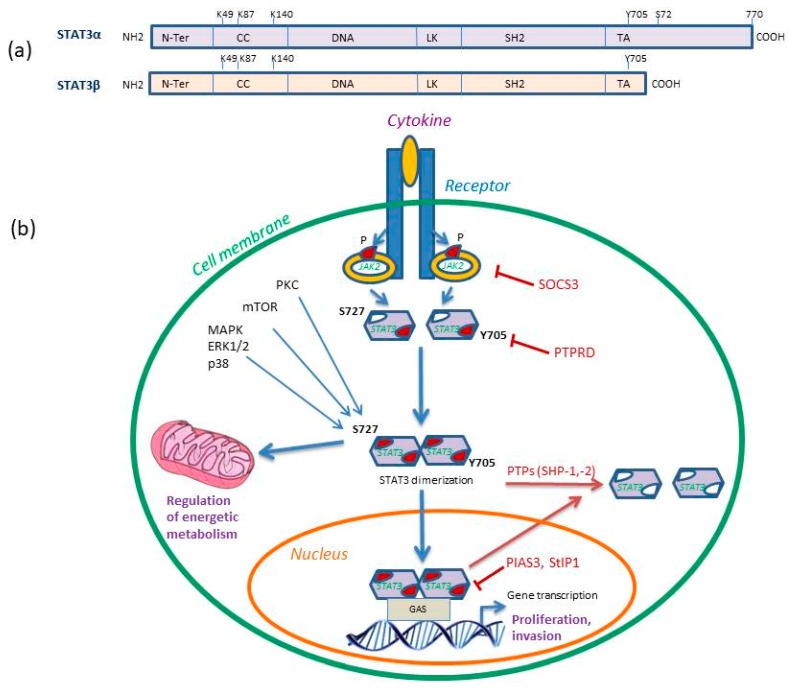
Figure 1.
(a) STAT3 isoforms structural domains. Both isoforms consist of the N-terminal domain (N-Ter), a coiled coil (CC), a DNA binding domain (DNA), a linker domain (LK), the Src homology 2 (SH2) and the C-terminal transactivation domain (TA) that contains the two phosphorylation sites Tyr-705 (Y705) and Ser-727 (S727) involved in gene transcription activity. The STAT3 K49 and K87 residues are targets of acetylation and K140 of methylation. (b) STAT3 signaling pathway in cancer. STAT3-Y705 phosphorylation is induced by JAK2 recruitment and phosphorylation. STAT3-S727 phosphorylation is mediated by PKC, MAPK or mTOR pathway and it can further regulate cell bioenergetics. Activated STAT3 homodimerizes and translocates to the nucleus where it binds gamma-activated sequences (GAS) to initiate gene transcription and regulation. The inhibitors of STAT3 signaling are shown, including suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS3) that inhibits JAK2, receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase delta (PTPRD) that dephosphorylates Y705 site and protein inhibitor of activated STAT3 (PIAS3) and STAT3 interacting protein (StIP1), which directly inhibit activated STAT3. The SH2-containing SHP-1 and SHP-2 protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPs) dephosphorylate pSTAT3-Y705 dimers and render them inactive. P represents phosphorylation. Reproduced/adopted in modified form from [19]. Copyright (Elsevier, 2017).