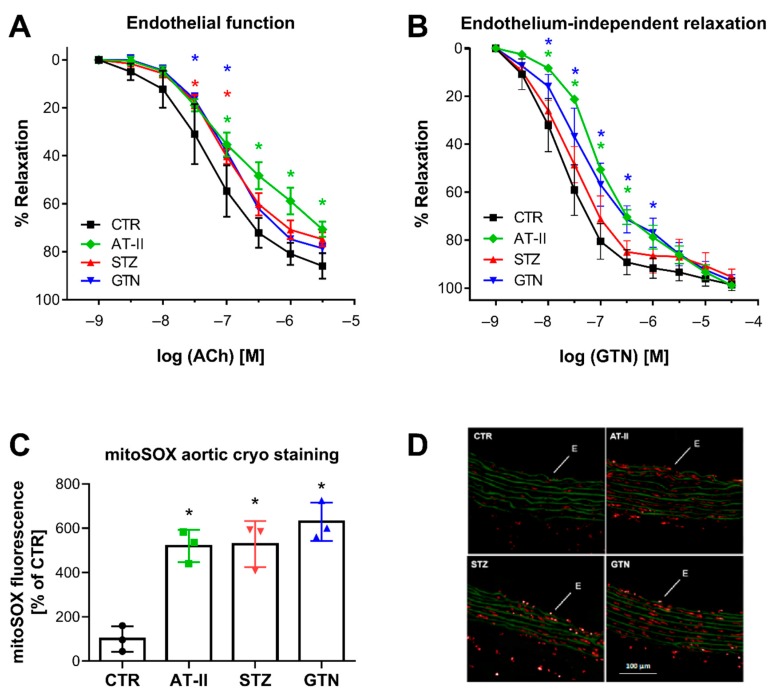
Figure 5.
Vascular function and ROS formation of aorta from rats with preestablished cardiovascular disease or pharmacologically induced oxidative stress. Endothelium-dependent relaxation (ACh-triggered) (A) and endothelium-independent relaxation (GTN-triggered) (B) was determined by isometric tension method in aortic ring segments of hypertensive, diabetic and nitrate tolerant rats, and respective control animals. (C) Vascular ROS formation was determined by mitoSOX oxidative fluorescent microtopography in aortic cryo-sections. Representative fluorescence images are shown with red fluorescence for mitoSOX oxidation products and green fluorescence for autofluorescence of the basal laminae (D). Data are mean ± SD of 7 (Ctr, A,B), 3 (AT-II, STZ, GTN, A,B) and 3 (C) rats per group. Each single animal data point was generated from 3–4 (A,B) or 3 (C) technical replicates. * p < 0.05 vs. control group.