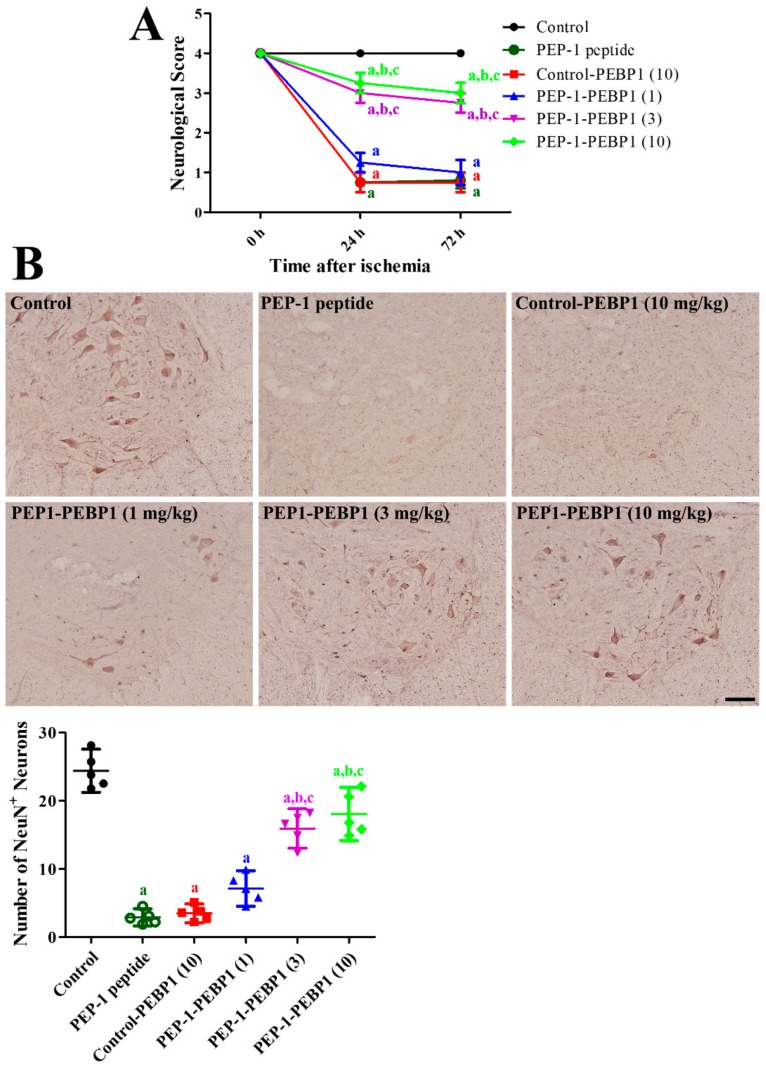
Figure 4.
Effect of PEP-1-PEBP1 protein against ischemic damage in the rabbit spinal cord. (A) Neurological deficits are assessed by Tarlov’s criteria 24 h and 72 h after reperfusion (n = 10 per group; a p < 0.05, significantly different from the control group, b p < 0.05, significantly different from the PEP-1 peptide-treated group; c p < 0.05, significantly different from the control-PEBP1-treated group). The bars indicate SEM. (B) Immunohistochemistry for NeuN to label the surviving neurons in the ventral horn of the spinal cord 72 h after ischemia/reperfusion. The number of NeuN-positive nuclei per section in all the groups is also shown (n = 5 per group; a p < 0.05, significantly different from the control group, b p < 0.05, significantly different from the PEP-1 peptide-treated group; c p < 0.05, significantly different from the control-PEBP1-treated group). The bars indicate confidence interval or standard errors of mean.