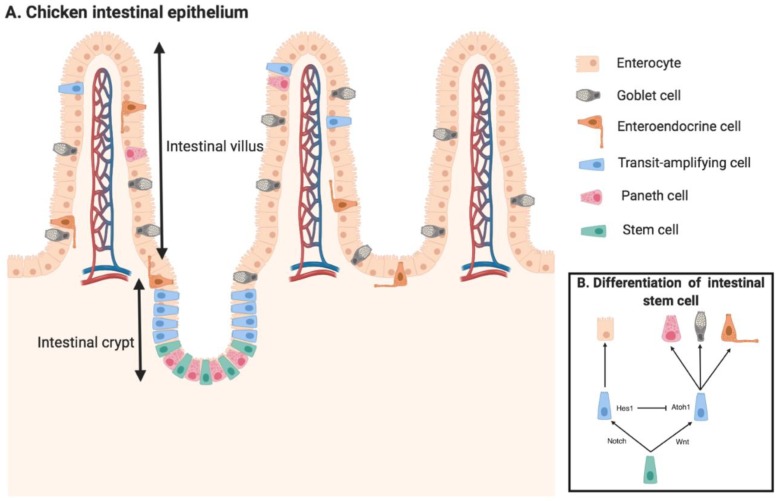
Figure 1.
Chicken small intestinal epithelium model. The chicken intestinal epithelium is a complex biosystem that has multiple functions. (A) The intestinal crypt invaginates as a pocket and the intestinal villus protrudes as a finger structure. Intestinal stem cells are located at the crypts and differentiate into transit-amplifying cells for further differentiation into mature epithelial cell populations (enterocytes, goblet cells, enteroendocrine cells, and Paneth cells). (B) The model for the differentiation of the intestinal stem cell is a process of the intermediate differentiation from stem cells to transit-amplifying (TA) cells, and the terminal differentiation from TA cells to absorptive enterocytes, secretory goblet, Paneth, and enteroendocrine cells, which is mediated by the synergistical regulation of Notch and Wnt signals.