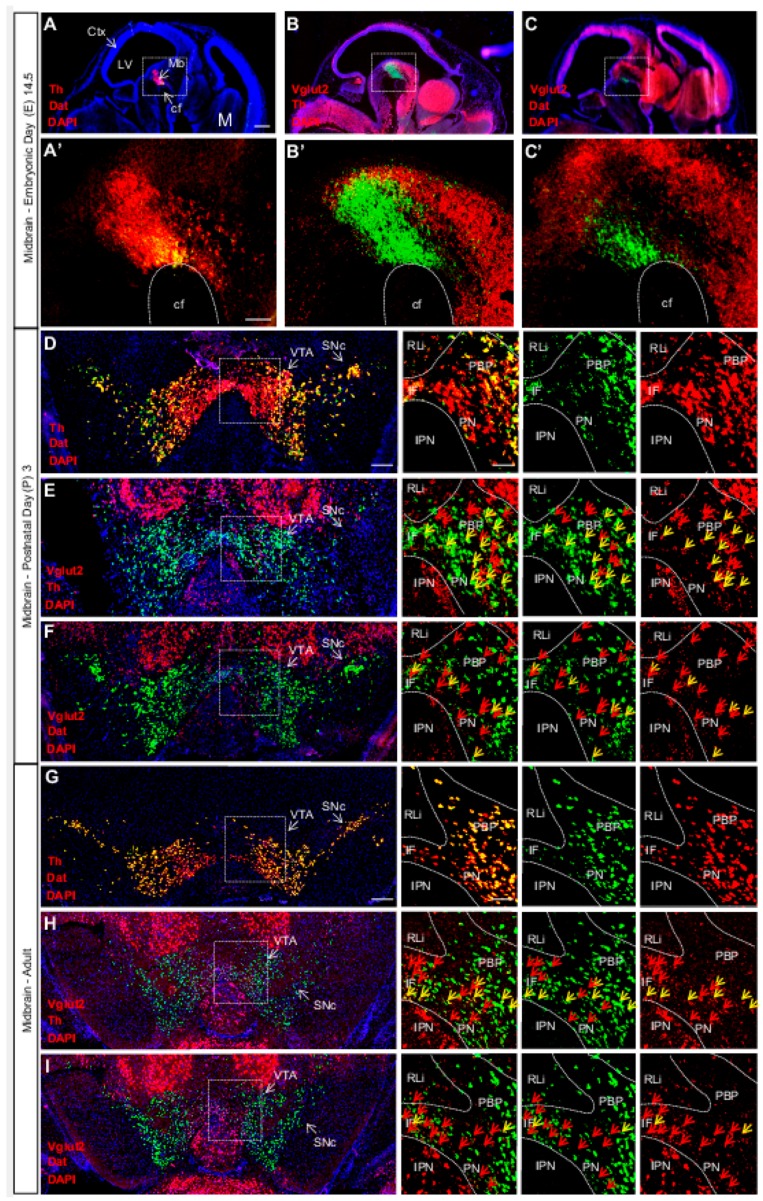
Figure 3.
Vglut2, Th and Dat mRNA co-localization within certain VTA dopamine (DA) neurons is sparse at E14.5, peaks around birth and is subsequently down-regulated in adulthood. Double fluorescent in-situ hybridization for Th (red), Dat (green) and Vglut2 (red) mRNA, respectively, on wildtype mouse midbrain sections. (A–C) Sagittal sections of E14.5 embryo. Dotted square around the area of developing midbrain DA neurons (A–C) with close-ups in (A’–C’). (A) Th and Dat mRNA show co-localization (yellow) in the ventral midbrain (scale bar 500 mm). (A’) higher magnification of insets (scale bar 100 mm); (B,B’) Th and Vglut2 mRNA expression in the midbrain. (C,C’) Dat and Vglut2 mRNA show sparse detection in the midbrain. (D–F) Coronal sections of ventral midbrain in pups of postnatal day (P) 3. (D) Th and Dat show ample co-localization (yellow) in the lateral VTA and SNc (scale bar 250 mm, inset 100 mm). (E) Th and Vglut2 mRNA and (F) Dat and Vglut2 mRNA prominently co-localize (yellow) at this age in the IF, PBP and PN areas (arrows) but not in the RLi of the VTA. (G–I) Coronal sections of the adult midbrain (10 weeks; scale bar 250 mm, inset 100 mm). (G) Th and Dat mRNA co-localization (yellow) remains strong; whilst the level of co-localization between (H) Th and Vglut2 and (I) Dat and Vglut2 mRNAs is lower than at P3 (arrows). Yellow arrows show co-localization green (Dat) and red (Vglut2) channel, red arrows show red (Vglut2) channel (Postnatal Day (P) 3 n = 3; adult n = 3). Abbreviations: cf, cephalic flexture; Ctx, cortex; IF, interfascicular nucleus; IPN, interpeducular nucleus; LV, lateral ventricle; M, medulla; Mb, midbrain; PBP, parabrachial pigmented area; PN, paranigral nuclei; RLi rostral linear nucleus; SNc, Substantia nigra pars compacta; VTA, Ventral tegmental area. Reprinted from Papathanou et al., 2018 [24].