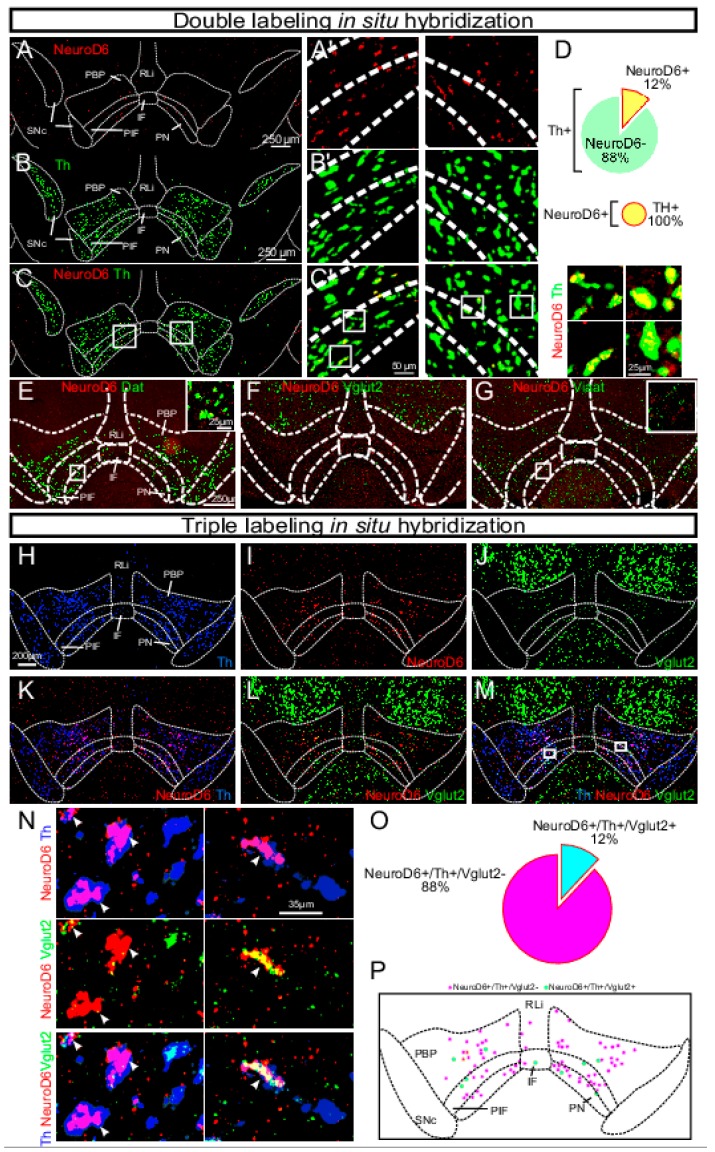
Figure 10.
NeuroD6 mRNA is found in a modest population of the VTA and co-localizes with dopaminergic markers and partially with a glutamatergic marker. (A–G) Double FISH in the ventral midbrain of adult wild-type mice detecting the following mRNAs. A, A’, NeuroD6 (red). (B,B’) Th (green). (C,C’) NeuroD6 (red) and Th (green). Th/NeuroD6 mRNA that overlap are shown in yellow. Low magnification to the left; close-ups to the right. Schematic outline shows borders for SNc and subregions of VTA: PN, PIF, PBP, IF, RLi. (D) Quantification of percentage of NeuroD6-positive cells among all Th VTA cells; all NeuroD6 cells are positive for Th mRNA. (E) NeuroD6 (red) and Dat (green), inset with high magnification of Dat/NeuroD6 mRNA overlap (yellow). (F) NeuroD6 (red) and Vglut2 (green). (G) NeuroD6 (red) and Viaat (green), inset with high magnification of Viaat-negative/NeuroD6-positive (red). (H–P) Triple-labeling FISH in the ventral midbrain of adult wild-type mice detecting: (H) Th (blue); (I) NeuroD6 (red); (J) Vglut2 (green) mRNAs and their co-localization: (K) NeuroD6/Th; (L) NeuroD6/Vglut2; (M) Th/NeuroD6/Vglut2. Cellular closeups: (N) NeuroD6/Th (top), NeuroD6/Vglut2 (middle), and Th/NeuroD6/Vglut2 (bottom). Arrows point to NeuroD6 mRNA-positive cells. (O) Quantification of percentage of NeuroD6+/Th+/Vglut2+ and NeuroD6+/Th+/Vglut2- neurons of the VTA. (P) Schematic illustration of distribution pattern of NeuroD6+/Th+/Vglut2+ and NeuroD6+/Th+/Vglut2- neurons within the VTA (same as shown with experimental data in M). NeuroD6+/Th+/Vglut2- cells in magenta; NeuroD6+/Th+/Vglut2+ cells in cyan. VTA, ventral tegmental area; SNc, substantia nigra pars compacta; PBP, parabrachial pigmented nucleus; PN, paranigral nucleus; PIF, parainterfascicular nucleus; RLi, rostral linear nucleus; IF, interfascicular nucleus. FISH, fluorescent in situ; Dat, Dopamine transporter; Th, Tyrosine hydroxylase; Vglut2, Vesicular glutamate transporter 2; Viaat, Vesicular inhibitory amino acid transporter. Reprinted from Bimpisidis et al., 2019 [102].