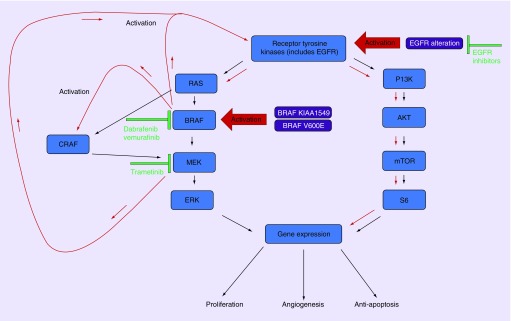
Figure 2. . RTK/MAPK feedback pathways of RAS/P13K following BRAF and MEK inhibition.
Inhibition of BRAF leads to reduced ERK-dependent feedback and increase activation of RTK and activation of alternative RAF, such as CRAF which stimulates MEK resulting in reactivation of the MAPK pathway. Inhibiting MEK concurrently with BRAF helps prevent reactivated MAPK pathway but results in increased activation of RTK and increased P13K/AKT pathway activation, which can result in treatment resistance. Alterations in EGFR that result in amplification may result in resistance to BRAF inhibition and are a possible concurrent therapeutic target. Red arrows indicate an increase of activation of pathways.
AKT: Protein kinase B; BRAF: Proto-oncogene B-Raf; CRAF: Proto-oncogene c-RAF; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin; P13K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; RTK: Receptor tyrosine kinase; S6: p70 ribosomal protein S6 kinase.