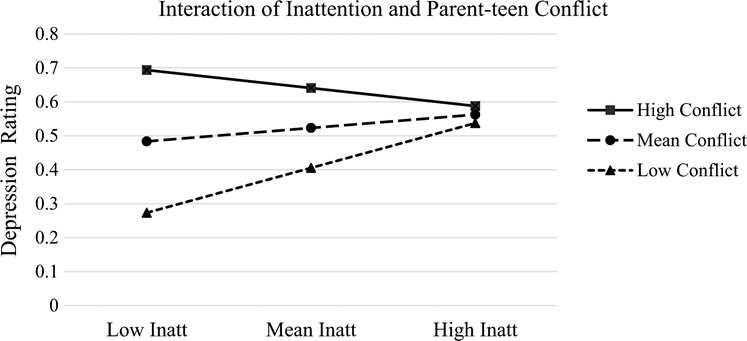
Fig. 1.
Interaction of inattention and parent–teen conflict predicting withdrawal/depression. Note High/low inattentive symptoms = ± 1 SD inattention, respectively, from disruptive behavior disorders rating scale; high/low conflict = ± 1 SD, respectively, from conflict behavior questionnaire; depression score = mean rating from youth self-report withdrawn/depressed score