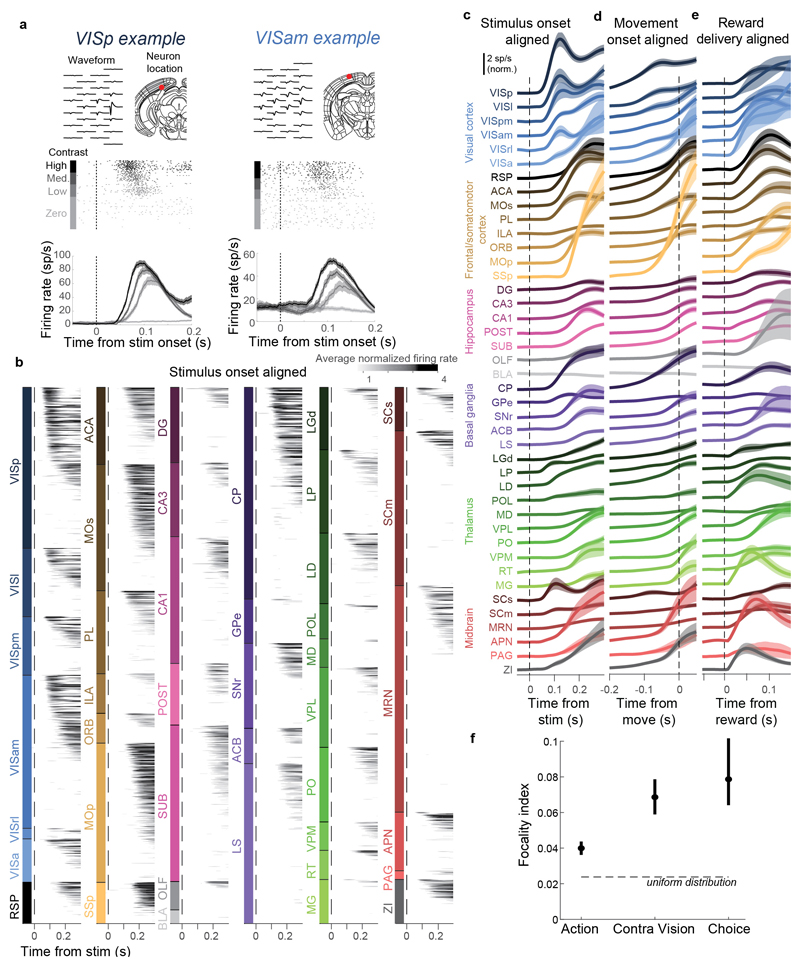
Extended Data Figure 4. Global activity of individual neurons during task performance; global activity during the task and following reward delivery; and ‘focality index’ analysis of coding distribution.
a, Activity of example neurons in VISp and VISam, showing the neuron’s waveform and anatomical location (top), rasters sorted by contralateral contrast (middle), and trial-averaged firing rates (smoothed with 30 ms causal half-Gaussian) for each of the four contralateral contrasts (bottom). Shaded regions: +/- s.e. across trials. b, Colormap showing trial-averaged firing rates of all highly-activated neurons (p<10-4 compared to pre-trial activity), vertically sorted by firing latency. Latency sorting was cross-validated: latencies for each neuron were determined from odd-numbered trials, and activity from even-numbered trials is depicted in the plot. Gray scale represents average normalized firing rate across even-numbered trials with contralateral visual stimuli and movement. c-e, Curves showing mean firing rate across responsive neurons in each area, aligned to visual stimulus onset (c), movement onset (d), or reward onset (e). Shaded regions: ± s.e. across neurons. f, The focality index, defined as where pa is the proportion of neurons in area a selective for the kernel in question, measures how widely versus focally distributed a representation is, with a floor of 0.0238 for a uniform distribution (across 42 brain regions) and a max of 1.0 if all selective neurons were found in a single brain region. This focality index was 0.079 for choice, 0.069 for visual kernels and 0.040 for action kernels; the differences between Choice and Move, as well as Contralateral Vision and Action, were statistically significant (p<0.05; bias-corrected bootstrap). Dots represent the true value and error bars represent bias-corrected bootstrap-estimated 95% confidence intervals. Brain diagrams were derived from the Allen Mouse Brain Common Coordinate Framework (version 3 (2017); downloaded from http://download.alleninstitute.org/informatics-archive/current-release/mouse_ccf/).