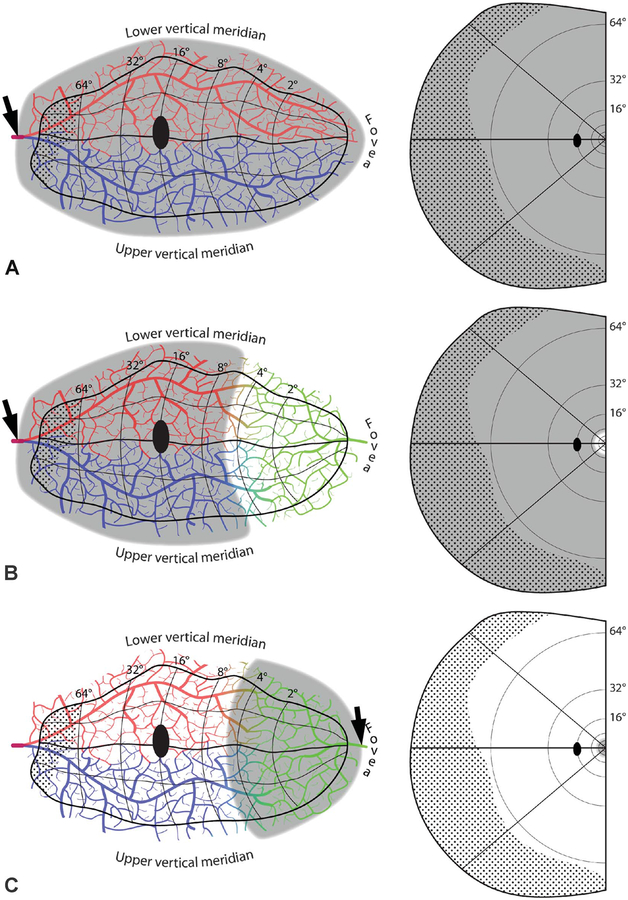
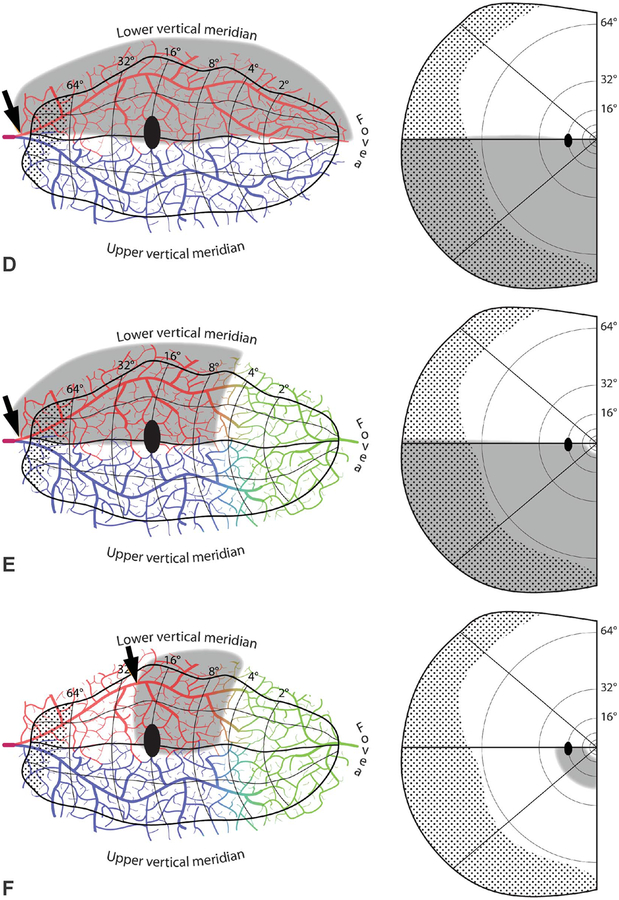
FIG. 5.
Embolic cortical visual field defects. A. Complete homonymous hemianopia from an embolus (arrow) proximal to the bifurcation of the superior (red) and inferior (blue) calcarine arteries. B. Homonymous hemianopia with macular sparing, owing to collateral flow from the distal middle cerebral artery (green). C. Hemimacular scotoma from an embolus occluding distal branches from the middle cerebral artery. D. Quadrantanopia from an embolus distal to the bifurcation of the calcarine artery. The border between the vascular territories of the superior and inferior calcarine arteries is placed arbitrarily along the horizontal meridian. E. Quadrantanopia with macular sparing. F. Quadrantanopia with both macular and peripheral sparing, from an embolus lodged distally in a calcarine artery branch.