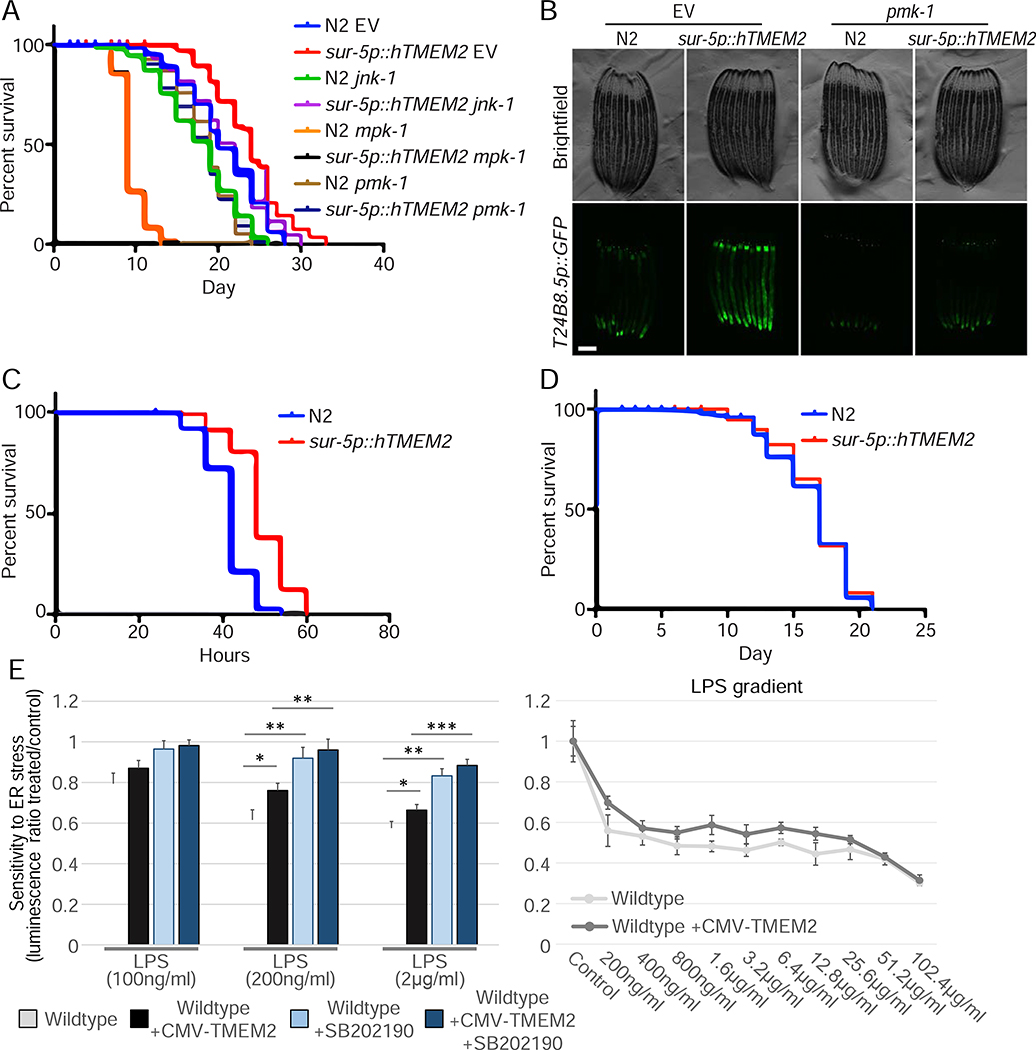
Figure 6:
hTMEM2 overexpression promotes immunity and extends lifespan through mpk-1/pmk-1. A) Lifespans were measured in Wildtype and sur-5p::hsf-1 animals on EV, jnk-1, mpk-1, or pmk-1 RNAi from hatch. Data is representative of three independent trials. B) Fluorescent micrographs of Wildtype (N2) and sur-5p::hTMEM2 animals expressing the immune response reporter, T24B8.5p::GFP. Animals were grown on EV or pmk-1 RNAi as described in STAR METHODS. Data is representative of three independent trials. C) Survival was scored in Wildtype (N2) and sur-5p::hTMEM2 animals exposed to PA14 infection at L4. Survival was scored every 6 hours as described in STAR METHODS. Data is representative of two independent trials. D) Lifespans were measured in Wildtype (N2) and sur-5p::hTMEM2 animals grown on dead EV RNAi from hatch. Bacteria were killed by UV irradiation, as described in STAR METHODS. All statistics for C-D were performed using Log-Rank (Mantel-Cox) test using PRISM, and are available in Supplemental Table 2. E) Wildtype and CMV-TMEM2 overexpressing human fibroblasts were exposed to lipopolysaccharides (LPS) derived from the E. coli bacteria strain (O111:B4). Resistance to the presence of LPS was measured through CTG to determine the cell density after 5 days of exposure; (n=3). Statistical analysis: One-way ANOVA test with a post-hoc Bonferroni-Holm analysis