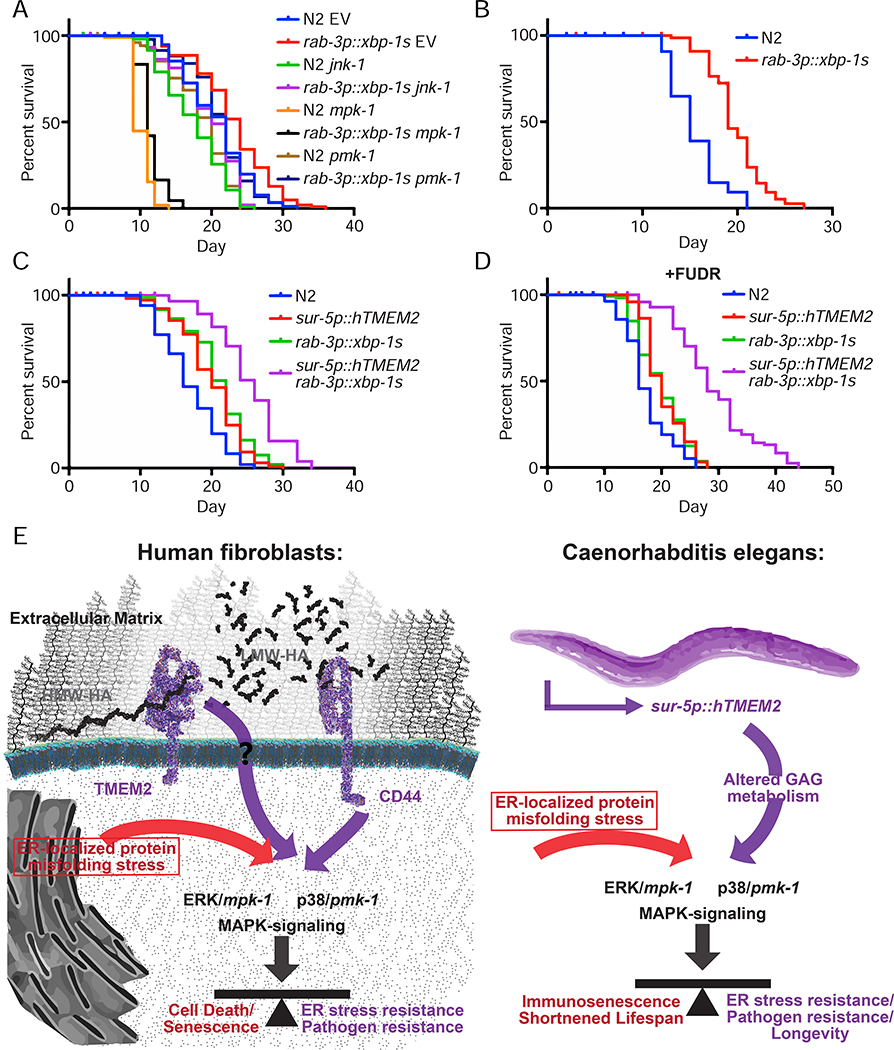
Figure 7:
Lifespan extension through canonical xbp-1s signaling is not dependent on mpk-1/pmk-1 and is distinct from hTMEM2. A) Lifespans were measured in Wildtype (N2) and rab-3p::xbp-1s animals on EV, jnk-1, mpk-1, or pmk-1 RNAi from hatch. Data is representative of three independent trials. B) Lifespans were measured in Wildtype (N2) and rab-3p::xbp-1s animals grown on dead EV RNAi from hatch as per 5D. Data is representative of two independent trials. C-D) Lifespans were measured in Wildtype (N2), sur-5p::hTMEM2, rab-3p::xbp-1s, and sur-5p::hTMEM2/rab-3p::xbp-1s animals in the absence (C) and presence (D) of FUDR. Animals were grown on EV RNAi from hatch, and the assay was either performed on standard EV plates (C) or moved to FUDR containing plates at L4 for (D) - see STAR Methods for details. E) Graphical representation of the key insight generated by this work. In human fibroblasts, TMEM2 breaks down HMW-HA into LMW-HA within the ECM. Through interaction with CD44, LMW-HA influences ERK/mpk1- and p38/pmk-1-mediated MAPK-signaling. This in turn alters ER stress resistance and pathogen resistance in human fibroblasts. In C. elegans, TMEM2-mediated changes to glycosaminoglycan (GAG) metabolism cause a shift in MAPK signaling. This in turn alters the response to ER stress and with it, changes pathogen resistance and the lifespan of the animals.