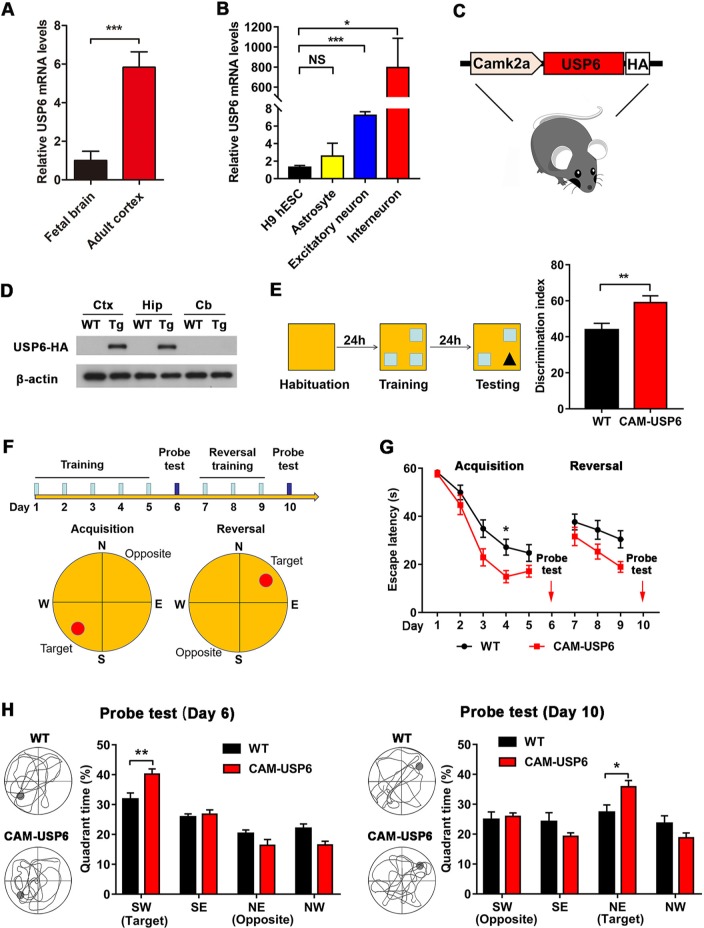
Fig 1. Transgenic USP6 expression enhances learning and memory in mice.
(A) USP6 mRNA levels in the cortex of fetal and adult human brains were quantified by qRT-PCR. The data represent means ± SEM, n = 5. ***P < 0.001 determined by Student t test. (B) USP6 mRNA levels in H9 hESCs, human astrocytes, induced human excitatory neurons, and interneurons were quantified by qRT-PCR. Data represent means ± SEM, n = 15. **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001 determined by nonparametric test (Kruskal-Wallis test) with Dunn’s post hoc analysis. (C) Schematic diagram of the USP6 transgene under the regulation of a CamK2a promoter (CAM-USP6). (D) Immunoblot analysis of USP6-HA expression in the cortex, hippocampus, and cerebellum of CAM-USP6 mice. (E) Schematic diagram and results from NOR test analysis. Data represent means ± SEM. WT: n = 16 mice, CAM-USP6: n = 16 mice. **P < 0.01 determined by Student t test. (F) MWM assessment of spatial memory and reversal learning. (G) MWM test results depicting escape latency as defined by the time taken to find a hidden platform. Data represent means ± SEM. WT: n = 16 mice, CAM-USP6: n = 16 mice. *P < 0.05 determined by repeated-measures ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc analysis. (H) MWM and reversal learning probe test results, acquisition phase: the target located in the SW quadrant; reversal learning: the target located in the NE quadrant. Data represent means ± SEM. WT: n = 16 mice, CAM-USP6: n = 16 mice. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 as determined by Student t test. The underlying data for this figure can be found in S1 Data. CAM, CamK2a; CamK2a, calcium/calmodulin dependent protein kinase II alpha; Cb, cerebellum; Ctx, cortex; HA, hemagglutinin; hESC, human embryonic stem cell; Hip, hippocampus; MWM, Morris water maze; NE, northeast; NOR, novel object recognition; NS, not significant; NW, northwest; qRT-PCR, quantitative reverse transcription PCR; SE, southeast; SW, southwest; Tg, transgenic; USP, ubiquitin-specific protease; WT, wild-type.