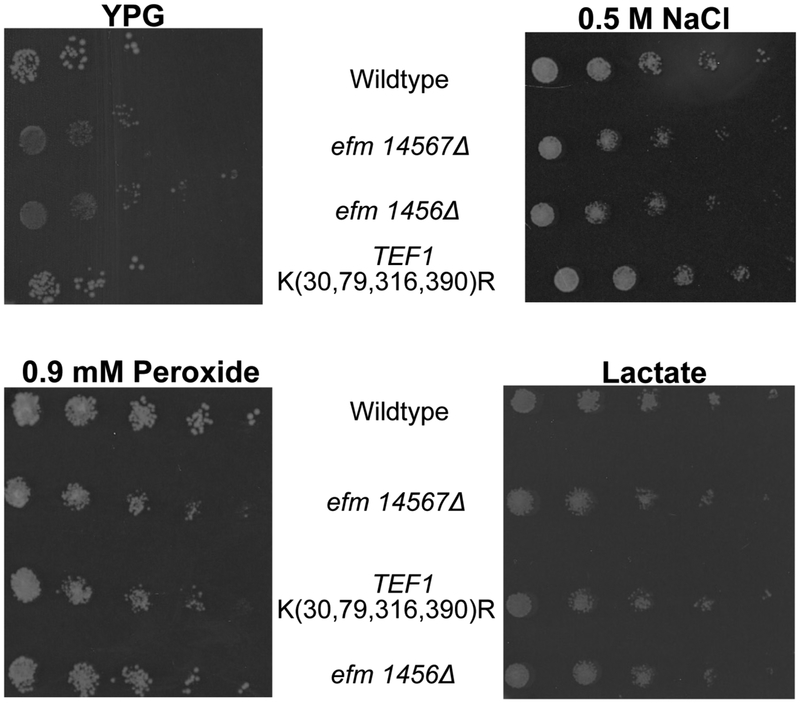
Figure 4: Loss of Efm methyltransferases causes sensitivity under different cellular stress conditions.
Representative images showing yeast cells that were grown in YPD, serially diluted and then spotted on YPD agar containing 0.5 M NaCl, or 0.9 mM peroxide, or YPG, or lactate media at 30 °C as described in the Figure 3 legend. Colonies were imaged after 2 days. In YPG, colonies for the efm1456Δ and efm14567Δ mutant were significantly smaller than wildtype colonies in 2 out of 3 replicate experiments whereas the TEF1 K(30,79,316,390)R mutant always grew relatively the same as wildtype in those replicates. Under oxidative stress, colonies for the efm1456Δ and efm14567Δ mutant were significantly smaller than wildtype colonies in 3 replicate experiments whereas the TEF1 K(30,79,316,390)R mutant always grew relatively the same as wildtype in three replicates. In the presence of sodium chloride, mutant colonies were smaller compared to wildtype in four replicate experiments. No difference in colony size was observed in lactate media for six replicates.