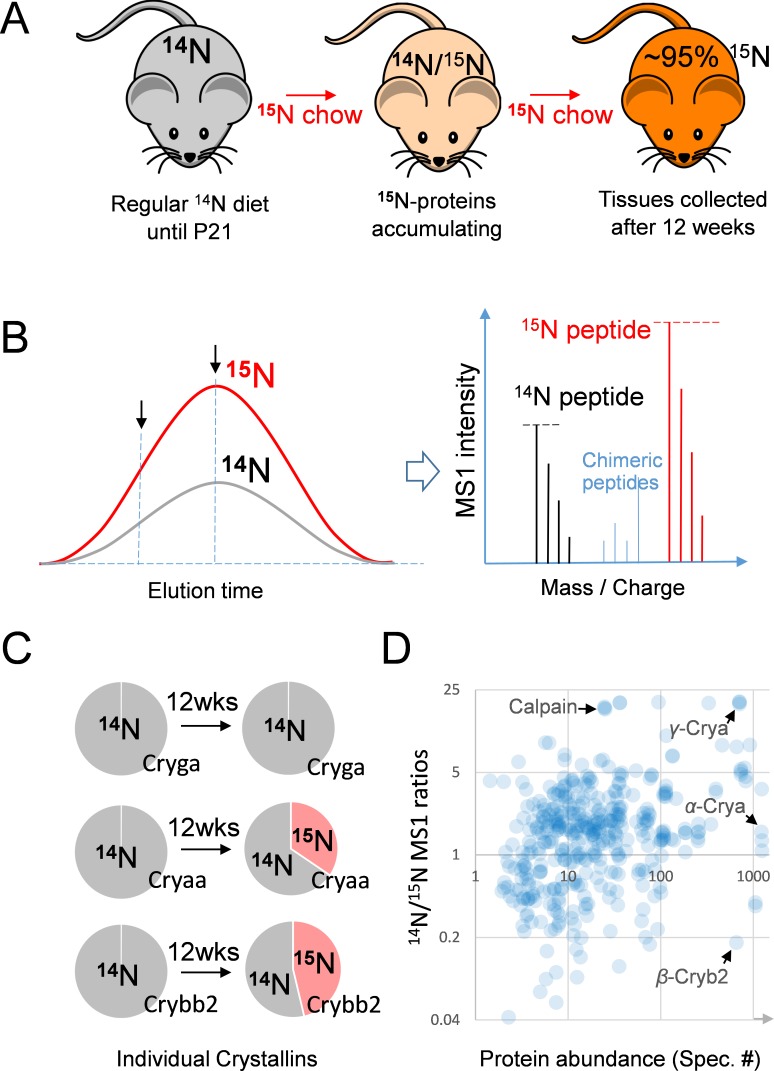
Figure 1. The 15N-labeling workflow for measuring the protein dynamics.
(A) After weaning, C57BL/6J mice were subjected to an exclusively 15N chow diet starting at P21 for a total duration of 12 weeks. 15N was incorporated into newly synthesized proteins. (B) In LC-MS/MS, 14N- and 15N-peptides of the same sequence co-elute (left panel). Regardless of where MS/MS is triggered (arrows pointing at random positions), the MS1 peptide signal intensities between the 14N and 15N channels reflect of their relative abundance (right panel). (C) Representative proteins showed different turnover rates. D. Among 543 lens proteins (blue dots) that were quantified via their 14N vs. 15N ratios (y-axis), there was a wide range of total protein abundance as estimated by MS/MS spectral counts (x-axis). Note that Calpain protease was long-lived, and the highly abundant α-, β- and γ-Crystallin proteins each had different levels of 14N and 15N.