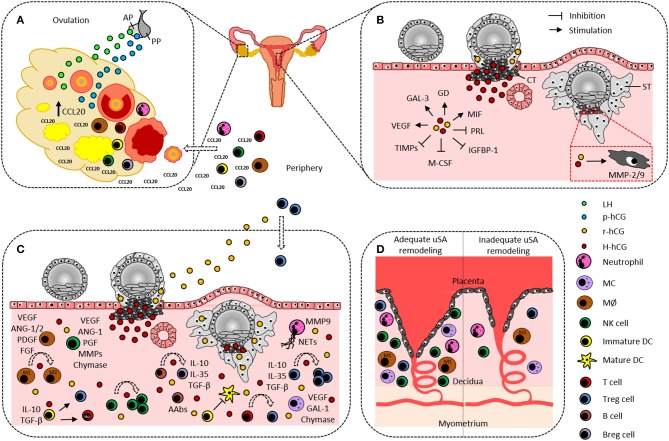
Figure 1.
Hypothetical scenario on the participation of human chorionic gonadotropin and immune cells in ovulation and embryo implantation. (A) Pituitary gland-produced LH and p-hCG induce ovarian CCL20 secretion that in turn promotes leukocyte influx from the periphery into the ovary. Ovarian DCs and MØ are suggested to actively contribute to the ovulation process. (B) Cytotrophoblast-derived H-hCG and syncytiotrophoblast-derived r-hCG promote angiogenesis, trophoblast invasion, and tissue-remodeling by inducing endometrial expression of GAL-3, GD, MIF, and VEGF as well as trophoblastic expression of MMP-2 and−9, and by inhibiting endometrial expression of PRL, IGFBP-1, M-CSF, and TIMPs. (C) Decidual innate and adaptive immune cells support embryo implantation by producing and secreting a variety of factors that are indicated aside each immune cell type and are partially induced by hCG. Additionally, hCG confers fetal tolerance by enhancing uterine NK cells, M2 cells, tolerogenic DCs, Th2 cells, Treg, and Breg, by promoting NETs formation by neutrophils, and by inducing fetal-protective AAbs in B cells. (D) Neutrophils, MØ, MCs, NK cells, and Treg cells are proposed to support uSA remodeling and fetal nourishment. A lack or dysfunctionality of these immune cells may result in improper uSA remodeling followed by fetal undernourishment and fetal growth restriction. AAbs, asymmetric antibodies; ANG-1/2, angiopoietin-1/2; AP, anterior pituitary gland; Breg, regulatory B cell; CCL20, CC-chemokine ligand 20; CT, cytotrophoblast; DC, dendritic cell; PDGF, platelet derived growth factor; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; GAL-1/3, galectin-1/3; GD, glycodelin; IGFBP-1, insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1; H-hCG, hyperglycosylated human chorionic gonadotropin; IL, interleukin; LH, luteinizing hormone; MØ, macrophage; MC, mast cell; M-CSF, macrophage colony stimulating factor; MIF, migration inhibitory factor; MMP-2/9, matrix metalloproteinase-2/9; NETs, neutrophil extracellular traps; NK cell, natural killer cell; p-hCG, pituitary human chorionic gonadotropin; PGF, placental growth factor; PP, posterior pituitary gland; PRL, prolactin; r-hCG, regular human chorionic gonadotropin; ST, syncytiotrophoblast; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β; TIMPs, tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases; Treg, regulatory T cell; uSA, uterine spiral artery; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.