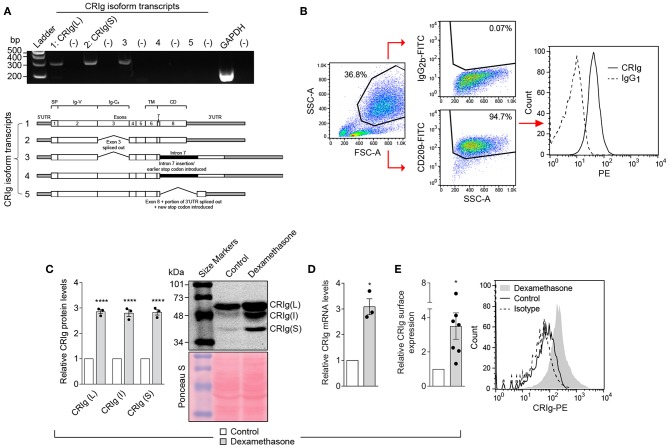
Figure 1.
CRIg expression in MDDC and effects of dexamethasone. (A) CRIg isoform transcripts detected in DC. Agarose gel electrophoresis (2%) was used to visualize transcript variant amplicons generated from the cDNA of HMDC. Lanes are labeled 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 representing each CRIg isoform with (–) to the right of each isoform lane indicating the respective no template controls. GAPDH was a positive control. Gels are representative of three experiments. (B) Gating strategy for CRIg expression on DC by flow cytometry. CD209+ cells were gated before assessing anti-CRIg antibody (6H8-PE) staining; representative histogram shown. (C) CRIg isoform expression by Western blot using anti-CRIg monoclonal antibody (clone 3C9). A representative blot of total protein stained with Ponceau S shows consistency of protein loading. Band intensity for each isoform (L, I, and S) over protein load was determined by densitometry. Data are expressed as fold-change over control DC (n = 3). (D) Relative CRIg mRNA expression as detected by qPCR, normalized to GAPDH, expressed as fold-change over control DCs (n = 3). (E) Relative CRIg cell-surface expression by flow cytometry. Data are expressed as fold-change in CRIg-PE (6H8) mean fluorescence intensity minus isotype control (IgG1) of treated over control DCs (n = 7); representative histogram shown. Data are presented as means ± SEM of experiments conducted with cells from different individuals. Significance levels are indicated by asterisks: *P < 0.05, ****P < 0.0001.