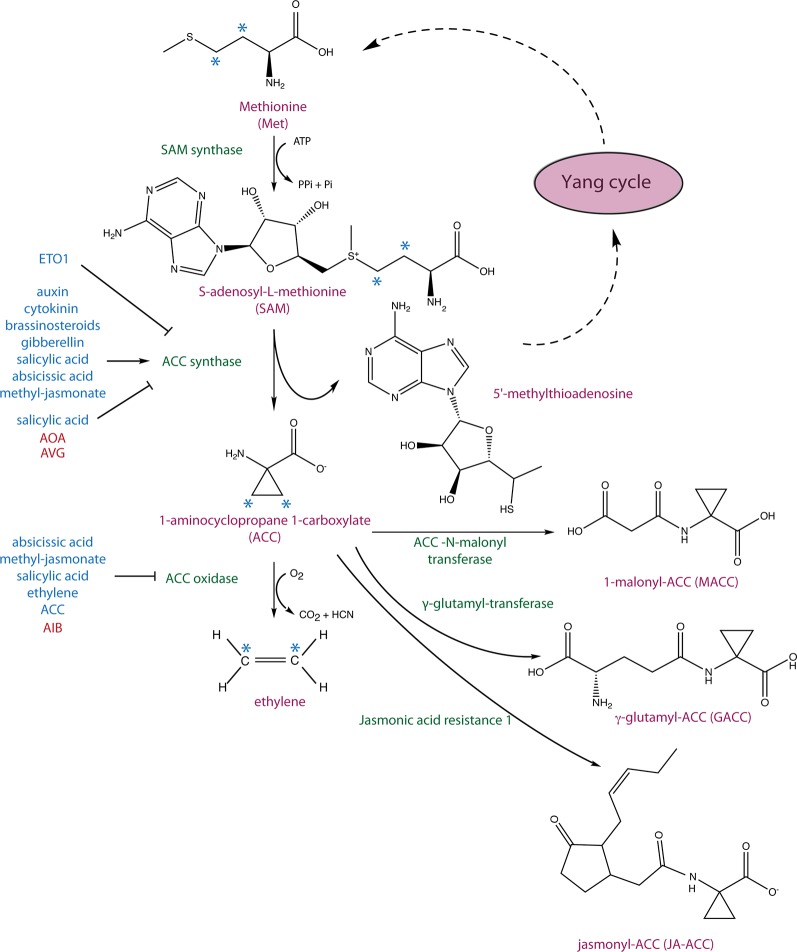
Figure 1.
Ethylene biosynthetic pathway and 1-aminocyclopropane 1-carboxylic acid (ACC) conjugation. S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM) synthase converts methionine to SAM, which is subsequently converted to ACC and 5’-methylthioadenosine (MTA) by ACC synthase (ACS). MTA is recycled back to the Yang cycle to recover methionine, and ACC is oxidized to ethylene by ACC oxidase (ACO). The hormonal inputs that regulate ACS and ACO expression as well as ACS stability are depicted in blue. ACC has been shown to be converted to three derivates: 1-malonyl-ACC (MACC) by the ACC-N-malonyl transferase, γ-glutamyl-ACC by a glutamyl-transferase, and jasmonyl-ACC (JA-ACC) by jasmonic acid resistance1 (JAR1). The asterisks mark carbons that give rise to ethylene.