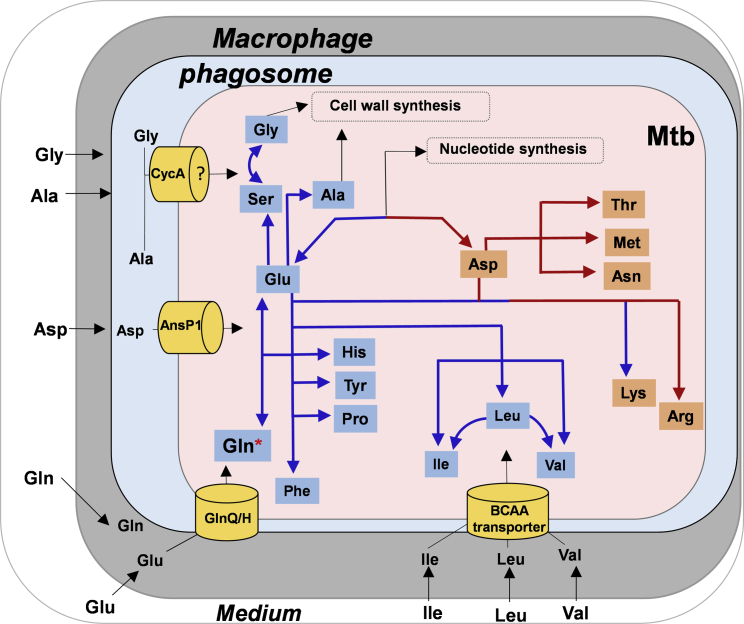
Figure 5.
Schematic Representation of Nitrogen Metabolism (Acquisition and Assimilation) in Intracellular Mtb
Macrophages acquires nitrogen sources Asp (aspartate), Glu (glutamate), Gln (glutamine), Leu (leucine), Ala (alanine), and Gly (glycine) directly from the growth media. Glu/Gln is taken from the host via yet-unidentified transporter. Asp is accessible to intraphagosomal Mtb, which it uptakes from the host macrophages via AnsP1 (Gouzy et al., 2014a). Leu, Ile (isoleucine), and Val (valine) are acquired from the host macrophages via yet-unindentified branched chain amino acid, probably an ABC-type transporter. Ala, Gly, and Ser are possibly acquired via CycA transport system. Gln, Val, and Asp were potential nitrogen donors for cellular protein synthesis, with Gln as the principal nitrogen donor in intracellular Mtb (indicated by asterisk). Nitrogen from Gln was transaminated primarily to Glu and Asp for the synthesis of other amino acids. Ala and Gly are assimilated mainly into Ala, Gly, and Ser pools. Limited transamination of nitrogen from Ala and Gly to other amino acids suggests direct assimilation of these two amino acids for biomass-cell wall synthesis.