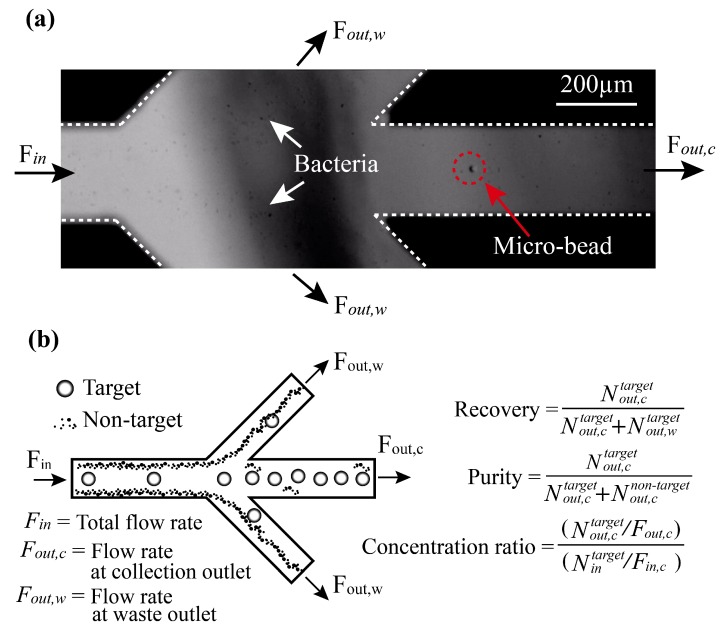
Figure 2.
Separation of aptamer-bound beads. (a) A high-speed camera (5000 fps) was used to observe the separation of cells. As a proof-of-principle demonstration, a mixture of aptamer-modified beads (9.6 µm) and bacteria (<1 µm) was infused into the sample inlet by one of the syringe pumps at a controlled flow rate of 500 µL/min (flow speed ~0.4 cm/s). The target and non-target were separated by acoustic radiation forces. The target was collected at the collection outlet and the non-target was moved to the waste outlet. (b) Definitions of the parameters used for evaluation of separation performance of the acoustofluidic device: Fin, total flow rate; Fout,c, flow rate at the collection outlet; Fout,w, flow rate at the waste outlet; Nin, total number of targets per second; Nout,c, number of targets per second at the collection outlet; , number of targets per second at the collection outlet; , number of non-targets per second at the collection outlet; , number of targets per second at the waste outlet; , number of non-targets per second at the waste outlet.