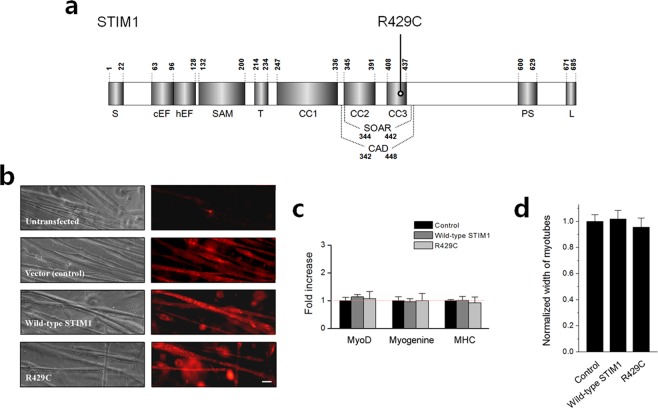
Figure 1.
Schematic of the primary structure of STIM1 and the expression of R429C in mouse primary skeletal myotubes. (a) Each domain of STIM1 is presented according to previous reports on the overall structure66, CAD/SOAR13,14,67, and CC domains35. The location of R429C is indicated. Numbers indicate the amino acid sequence. S, signal peptide; cEF, canonical EF-hand; hEF, non-functional hidden EF-hand; SAM, sterile α-motif; T, transmembrane domain; CC, coiled-coil domain; CAD/SOAR, Ca2+ release-activated Ca2+-activating domain/STIM1-Orai1-activating region; PS, proline/serine-rich domain; and L, lysine-rich domain. (b) Mouse primary skeletal myotubes that were untransfected or transfected with either cDNA of empty vector, wild-type STIM1, or R429C were stained with anti-GFP (for detecting CFP or CFP-tagged proteins) and Cy3-conjugated secondary antibodies. The bar represents 100 µm. (c) mRNA levels of MyoD, myogenin, and MHC in myotubes were analyzed by qRT-PCR. ‘Control’ means myotubes that were transfected with cDNA of empty vector (also for subsequent experiments). The normalized mean values of each to the mean value of the control are summarized as histograms. Difference was considered to be considerable at more than 2-fold increase and there was no considerable difference. The values are presented as the mean ± s.d. for triple experiments (Supplementary Table S1). (d) The width of myotubes was measured. The normalized mean values of each to the mean value of the control are summarized as histograms. Significant difference compared with the control (p < 0.05) and there was no significant difference in the width of the myotubes. The values are presented as the mean ± s.e.m. for the number of myotubes shown in parentheses in Table 1.