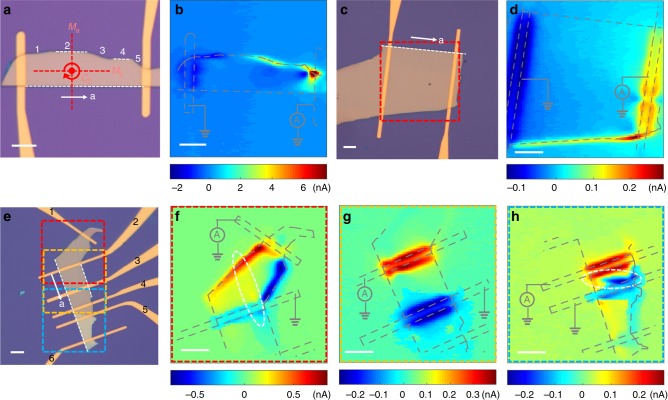
Fig. 2. Photocurrent response from edges along different directions.
a and b Optical microscope image (a) and scanning photocurrent image (b) of a device with irregular shape. c and d, Optical microscope image (c) and scanning photocurrent image (d) of a device with trapezium shape. e, f, g and h Optical microscope image (e) and scanning photocurrent image of different parts (f, g, and h) of a long device with edges along various crystal fracture directions. All measurements were excited with 180-μW 1.96-eV pulse laser. The white arrows in microscopy images mark the crystallographic -axis and the white dashed lines mark the edges that have no photocurrent responses. The red symbols in Figure (a) display the point group symmetries of the crystal lattice. Photocurrents only arise along edges that break the mirror symmetry, in good agreement with the symmetry analysis. The scale bars are all 8 μm.