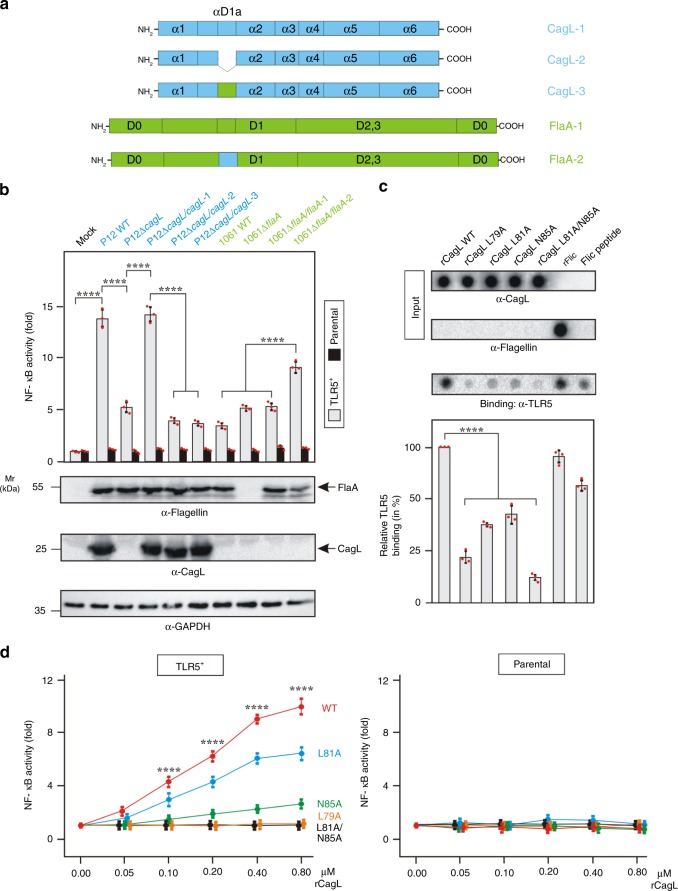
Fig. 3. H. pylori CagL contains a flagellin-mimetic motif that interacts with TLR5.
a Schematic representation of CagL and FlaAHp produced by deletion or swapping of the αD1a motif. b TLR5+ HEK293 cells were infected with the indicated H. pylori strains expressing the constructs shown in A, followed by quantification of NF-κB activity. c Protein binding assay. The indicated recombinant CagL proteins, FliC protein and FliC peptide as control were immobilized on Dotblots, followed by incubation with recombinant TLR5. Site-directed mutagenesis in the D1-motif of CagL reveals its importance in TLR5 binding as quantified densitometrically. d Dose-response curves of NF-κB activity in TLR5+ and parental cells treated with the indicated amounts of CagL proteins. EC50 value of WT CagL was determined to be 172.6 nM by using AAT Bioquest (https://www.aatbio.com). Mutations in the CagL D1-motif confirm its function in TLR5 activation. The CagL WT values are significant over all mutants as indicated. Quantitative data are shown as means ± SD. ****p < 0.0001 (one-way ANOVA). Each red dot represents a single data point. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.