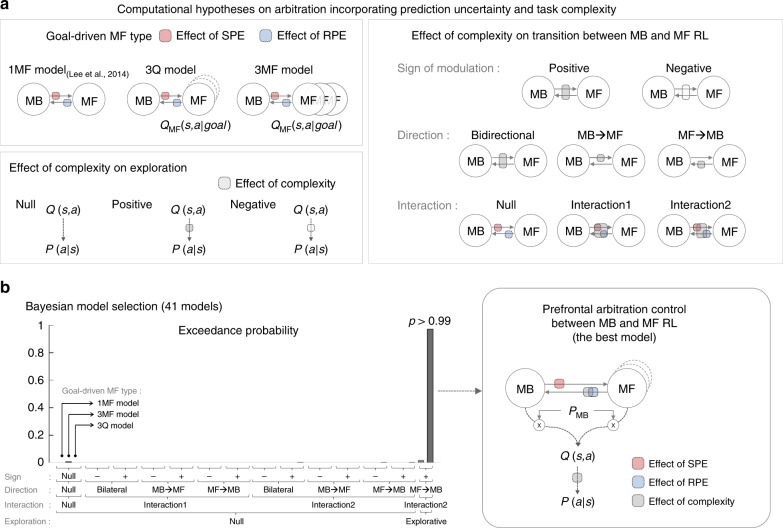
Fig. 5.
Model comparison analysis on behavioral data. a We ran a large-scale Bayesian model selection analysis to compare different versions of arbitration control. These model variants were broadly classified as reflecting the effect of complexity on the transition between MB and MF RL (13 = 1 + 2 × 2 × 3 types), the effect of complexity on exploration (3 variants), and the form of the MF controller (3 variants) each of which is classified by a type of goal-driven MF (3 types), an effect of complexity on transition between MB and MF RL, and an effect of complexity on exploration (3 types). Lee2014 refers to the original arbitration model30. b Results of the Bayesian model selection analysis. Among a total of 117 versions, we show only 41 major cases for simplicity, including the original arbitration model and 40 other different versions that show non-trivial performance (but the same result holds if running the full model comparison across the 117 versions). The model that best accounts for behavior is the version {3Q model, interaction type2, excitatory modulation on MF→MB, explorative} (exceedance probability >0.99; model parameter values and distributions are shown in Supplementary Table 1 and Supplementary Fig. 3, respectively).