Figure 3.
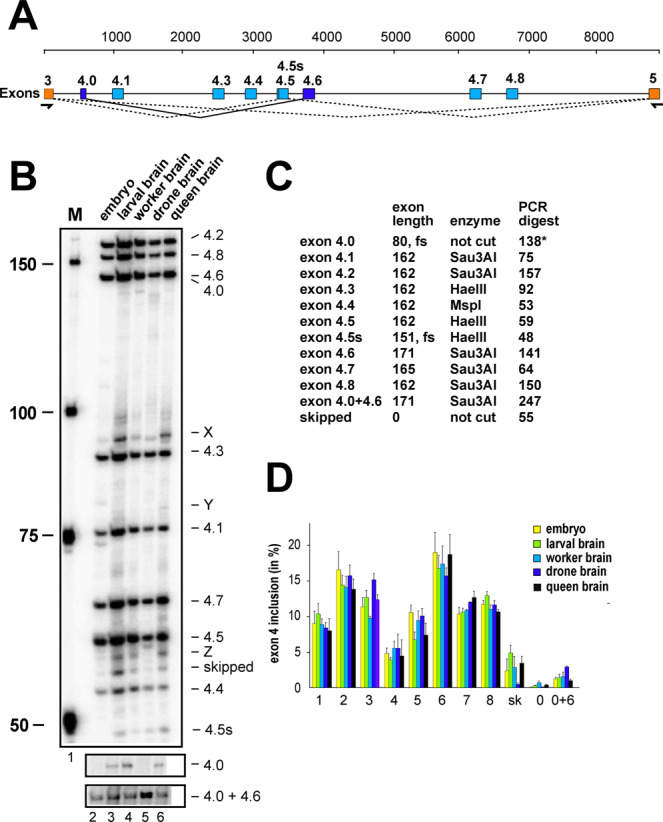
Apis mellifera Dscam exon 4 alternative splicing during bee development and between castes. (A) Schematic depiction of Apis mellifera Dscam exon 4 variable cluster with primers indicated below orange markes corresponding to constant exons 3 and 5. Variable exons 4 are marked in light blue. Newly discovered exon 4.0 is spliced to exon 4.6 (dark blue). An alternative 5′ splice site discovered in exon 4.5 is indicated as a line. (B) Denaturing polyacrylamide gels (6%) showing the splicing pattern of Dscam exon 4 isoform variables on top by digestion of a 32P labeled RT-PCR product with a combination of HaeIII, MspI, and Sau3AI restriction enzymes in embryos (line1), larval brains (line 2), worker brains (line 3), drone brains (line 4) and queen brains (line 5). Exon 4.0, that is close to exon 4.6 in length and exon 4.0 + 4.6 are shown from an undigested control (bottom). (C) Table showing the length of variable exons and their length after restriction digest with indicated restriction enzymes. Exon 4.0 is close to exon 4.6 in length and is shown from na undigested control gel in (B). (D) Quantification of inclusion levels of individual exons are shown as means with standard error from three experiments for embryos, larval brains, worker brains, drone brains and queen brains.
