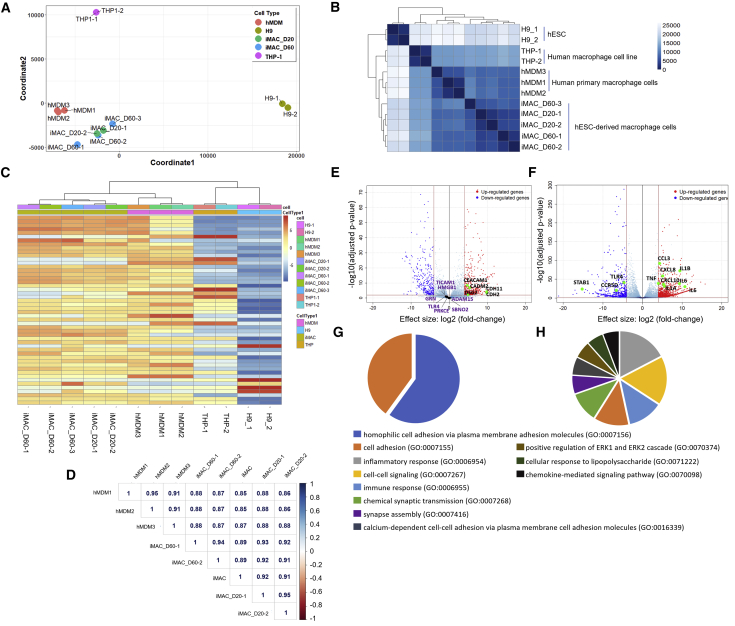
Figure 2.
Transcriptomic Characterization of iMACs Compared with Human Primary Macrophage
(A) Multidimensional scaling (MDS) analyses of the transcriptome of hESC-derived macrophages (iMAC-D20 and -D60) versus hESCs (H9), hMDMs, and THP-1 monocyte-differentiated macrophages. iMAC-D20 and -D60 are iMACs obtained on day 20 and 60 after differentiation, respectively. hMDMs are human peripheral blood monocyte (CD14+)-derived macrophages. Each circle represents an independent sample.
(B) Heatmap of sample-to-sample distance matrix using Poisson distance with hierarchical clustering, depicting overall similarity of transcriptome profiles of iMACs, H9, hMDMs, and THP-1 monocyte-differentiated macrophages. Color scale indicates Poisson distance values between samples.
(C) Unsupervised non-hierarchical clustering of samples and heatmap showing variance stabilizing transformation-normalized values of the top 50 variably expressed genes. The color key from blue to red indicates low to high expression values, respectively.
(D) Spearman coefficients of log2 normalized read counts. Left color bar indicates correlation scale (blue to red, 1 to −1).
(E and F) Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) of hMDMs versus iMACs (E) and hMDMs versus THP-1 (F), |log2(fold change)| > log 4, false discovery rate (FDR) < 0.01. Representative genes related to cell adhesion molecular pathway (E) and inflammatory responses (F) were indicated in the volcano plot. Purple gene names indicated immune-related genes (GO: 0002281) in (D).
(G and H) Functional categorization of DEGs based on gene ontology (GO) annotations. iMAC vs hMDM (G), Thp1 vs hMDM (H). GO terms are shown with FDR <0.0001. FDR is shown as −log10(FDR) < 0.0001.