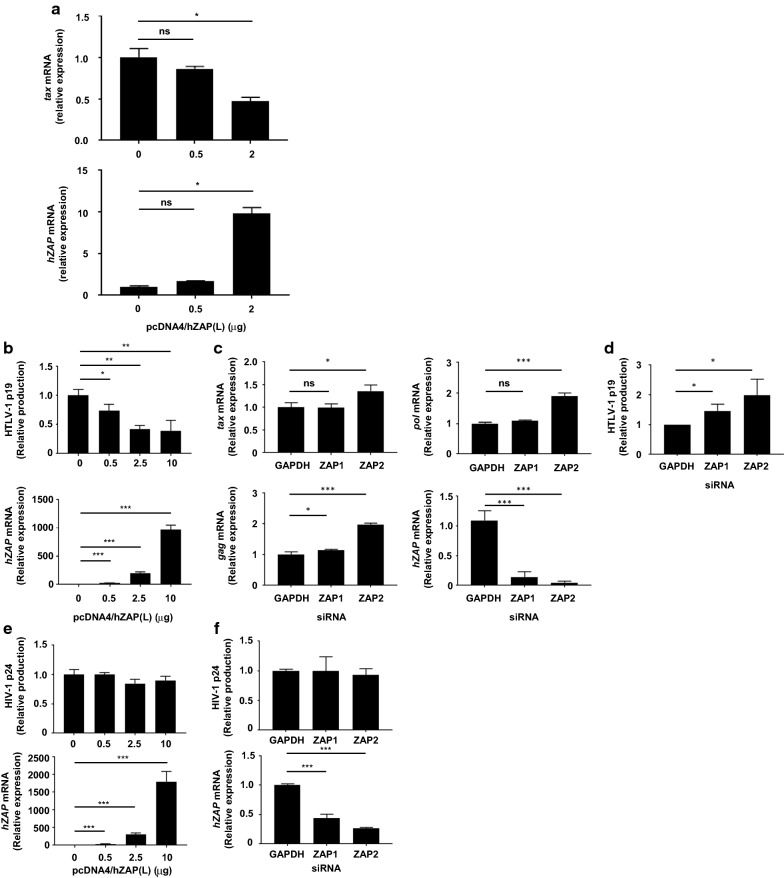
Fig. 4.
The involvement of ZAP in the regulation of HTLV-1 production. a HeLa cells were transfected with a Tax expression vector in the presence of increasing amounts of a ZAP expression vector. Changes in the level of tax transcripts (top) were measured by RT-qPCR, in addition to those of hZAP (bottom). *p < 0.0001. b JEX22 cells were transfected with increasing amounts of a human ZAP expression vector and cultured for 24 h. Stimulation with PMA/ionomycin was performed for 4 h before collecting the supernatant and cells for analysis. c, d JEX22 cells were transfected with the indicated siRNAs and cultured for 24 h. They were then stimulated, as indicated previously in this figure, before analysis. HTLV-1 RNAs (c) or p19 protein (d) was was measured (top panel) upon knock-down of endogenous ZAP (bottom panel). e J1.1 cells were transfected with increasing amounts of a human ZAP expression vector and cultured for 24 h. Stimulation with TNFα was performed for 4 h before collecting the supernatant and the cells for analysis. f J1.1 cells were transfected with the indicated siRNAs and cultured for 24 h. They were then stimulated as indicated before analysis. No significant changes were observed in p24 protein levels in the supernatant (top panel) upon knock-down of endogenous ZAP (bottom panel). *p < 0.05; **p ≤ 0.001; ***p < 0.0001