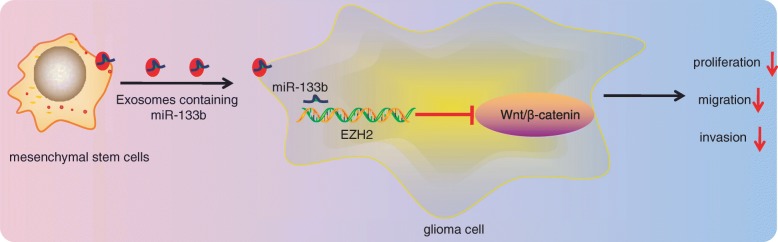
Fig. 8.
The schematic representation of mechanism by which MSC-derived exosomes containing miR-133b affect glioma cell activities. MSCs transfer miR-133b to glioma cells through exosomes to inhibit the EZH2 expression via suppression of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, whereby the glioma cell proliferation, migration, and invasion are diminished, and ultimately, the progression of glioma is attenuated